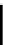Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
“alarms.” Counters are represented by a counter value. Hereby, OSEK OS takes care of periodically
incrementing this counter value. In case the counter value reaches a defined threshold, an alarm,
which is linked to the counter, can be triggered. his alarm can, for example, set an event or activate
a suspended task. To account for different modes of operations of an automotive real-time system,
OSEK OS provides different “application modes.” Each application mode owns its own subset of oper-
ating system entities (e.g., tasks, ISRs, etc.). During operation, a switch between these application
modes is possible.
18.3.2 OSEK NM
NM in the automotive area handles the “controlled coordinated start-up and shutdown” of the
communication of multiple ECUs within a network. he shutdown of the network (and the accom-
panying transitions of the ECUs into a low-power or even a power-down mode) is in general done
to reduce the network's power consumption in situations, where the functions performed by the
respective ECUs are not required (e.g., when the car is safely stored in a garage). Additionally, OSEK
NM [] provides (weakly-agreed) information on which ECUs within a network are participating
in the OSEK NM. This service is called “node monitoring” in OSEK NM. To realize these two ser-
vices, OSEK NM establishes a “logical ring” among all ECUs participating in OSEK NM. Along this
ring, OSEK NM “ring messages” are passed between the participating ECUs. These ring messages
contain information on whether the sending ECUs desires to perform a transition into a low-power
sleep mode. In case all ECUs along the logical ring agree on this transition (i.e., no ECU objects), a
coordinated transition into the sleep mode is performed. In case any ECU objects to this decision
since it still requires network operation, a transition into the sleep mode is prevented. Wakeup of a
sleeping network is triggered by any traffic on the network. Figure . depicts the state automaton
of OSEK NM.
In case an ECU, which is currently not a member of the logical ring, wants to join the ring to
participate in OSEK NM, the ECU's NM modules send a so-called “alive message” to introduce itself
NmOn
NmAwake
StopNm
NmBusSleep
NmShutdown
No Nm msg.
received
NmLimpHome
Communication Request
Nm msg.
received
No Nm msg.
received
NmNormal
Nm
inconsistency
detected
Nmlnit
NMReset
StartNm
Nm consistent
NmOff
Initial
Initial
Initial
FIGURE .
OSEK NM state automaton.