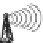Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
10.1 Introduction and Motivation
he main characteristics of wireless sensor networks [KW] can be explained by summarizing that
they are envisaged to be
•
Formed by tens to thousands of small, inexpensive sensors that communicate over a
wireless interface
•
Connected via base stations to traditional networks/hosts running applications interested
in the sensor data
•
Using multi-hop communications among sensors to bridge the distance between sensors
andbasestations
•
Considerably resource constrained due to limited availability of energy
To get an impression of the processing capabilities of a wireless sensor node, one should have the
following example of a sensor node in mind: a node running an -bit CPU at MHz clock frequency,
kB free of kB flash read only memory, bytes SRAM main memory, a . kbit/s radio interface
and the node being powered by battery.
Typical applications envisaged for wireless sensor networks are environment monitoring (earth-
quake or fire detection, etc.), home monitoring and convenience applications, site surveillance
(intruder detection), logistics and inventory applications (tagging and locating goods, containers,
etc.), as well as military applications (battleground reconnaissance, troop coordination, etc.). he fun-
damental communication pattern to be used in such a network consists of an application demanding
some named information in a specific geographical area. Upon this request, one or more base sta-
tions broadcast the request, and wireless sensors relay the request and generate answers to it if they
contribute to the requested information. he answers are then processed and aggregated as they flow
through the network toward the base station(s).
Figure . shows an exemplary sensor network topology as currently designated for such applica-
tions. he sensor network itself consists of one or more base stations that may be able to communicate
Classical infrastructure
Sensor network
...
Internet
Sensor node
Low power radio link
Base station
High bandwidth radio link
FIGURE .
General sensor network topology example.