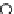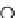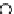Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
With such a mechanism, the sink may receive the same data several times from different paths.
For this reason a reinforcement scheme has been introduced, in order to use network bandwidth
more efficiently and thus to save energy. The reinforcement mechanism makes use of the data rate
parameter of the interest. In fact, at the beginning, the sink node broadcasts a low data rate inter-
est. When the gradient has been set up, i.e., when the sink starts receiving low data rate messages,
it reinforces one particular neighbor by increasing its data rate. When a node realizes that it has been
reinforced, it also has to reinforce at least one neighbor. From the sequence of reinforcements on
single hops, a high data rate path is established from the source of the events to the sink node.
The functioning of the Directed Diffusion routing protocol is shown in Figure ..
A convenient rule for the selection of the node to be reinforced has to be adopted in order to select
a low delay path. For example, a node might choose the neighbor from which more events have been
received, or the neighbor that regularly reports events before others. However, the path selected is
generally not optimum.
There is also a mechanism for negative reinforcements that change a high data rate to a low rate,
which can be used when a better path is found.
The reinforcement mechanism can also be used locally to repair failing or degraded paths. In this
case, the reinforcement is not triggered by the sink node, as an intermediate node can reinforce an
alternative link. However, this mechanism has to maintain alternative low data rate paths, so there is
a trade-off between robustness and energy efficiency.
Event
Source
Event
Source
Interests
Gradients
Sink
Sink
(a)
(b)
Event
Source
Sink
(c)
FIGURE .
Directed Diffusion protocol operations. (a) Interest propagation. (b) Initial gradients setup. (c) Data
delivery along reinforced path. (Redrawn from Intanagonwiwat, C., Govindan, R., and Estrin, D., Directed diffusion:
A scalable and robust communication paradigm for sensor networks, in
Proceedings of the th Annual ACM/IEEE
International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking
, pp. -, .)