what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
where
inf
denotes the inferior limit.
T
i
is exponentially distributed with rate
q
i
.
When the stochastic process leaves state
i
, it will next enter state
j
with probability
P
ij
, which is independent of the time spent at state
i
and satisfies
∑
⎧
⎪
⎪
P
=
1
ij
(3.25)
j
≠
i
P
=
0
ii
Also we have
q
q
ij
=
≠
P
(
i
j
)
(3.26)
ij
i
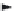
In this subsection, we propose a rate-based information low model on a network
G
(
n
,
w
,
τ
) based on the CTMC, in which each node is a state, the weight is repre-
sented as the transition probability, and the delay is represented as the staying time
in each state. Figure 3.3 illustrates an example of our model. We assume that the
information stays in a node
i
for a certain time period
T
i
before making a transition
to others. hen the information lows to other nodes
j
,
k
, and
l
according to transi-
tion probabilities
P
ij
,
P
ik
, and
P
il
.
3.3.2.1 Out-State Rate Estimation
Assume that the staying time at node
i
follows an exponential distribution with the
out-state rate
q
i
. According to the property of the exponential distribution, the expected
value of an exponentially distributed random variable
X
i
with rate
q
i
is given by
1
)
= =
E X
(
T
(3.27)
i
i
q
i
P
ij
j
P
ik
i
k
Stay in State
i
for Time
T
i
P
il
l
Figure3.3
Rate-basedinformationlowmodel.