what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
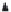
Eciency
Start of the
Crisis
Self
Organization
Formal
Organization
Crisis
Time
Figure 13.4
The dynamics of self-organization and institutional mechanism in
acrisissituation.(FromAssociatedPressstorybyMathewFordhahlin
Mercury
News
[http://radioresponse.org/wordpress/?page_id=46],October4,2005.)
situations, but the framework is still constant. he third type deals with complex sys-
tems that contain nondeterministic processes such as in the crisis example.
13.4 DesignofSociotechnicalSystems
he design process of a sociotechnical system is complex and time consuming.
In Reference 10 it explained a way of participatory design using sociotechnical
walkthrough. Documents are important in participatory design since they are
shared with the participants, and affect the decision making of each participant.
he documents should be accurate and up to date. How can these documents to
be produced? he sociotechnical walkthrough (STWT) can help to achieve this.
Also, to create such documents, a mix of abstract diagrams can be used. he prac-
tice shows that the STWT can support the participatory design process [10-12].
he participatory design is similar to groupware, which supports or modi-
ies the cooperation between different roles or persons. Due to the large number
of roles or persons, a lot of interactions, dependencies, and interference may occur
between them. hese may make the system much more complicated and not easy
to analyze.
13.4.1 STWT Concepts
he core idea of STWT is to build a diagrammatic model to represent a socio-
technical system. he model may be developed from scratch or derived from an
existing model. he model should be examined carefully step by step and be modi-
ied if necessary. Finally, the model should become the agreement of most of the
participants.