what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
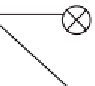
Figure12.4
InthemessagepropagationintheIMnetwork,thenodeswithblack
dotsrepresentthemessagecarriers,andthenodeswithcrossingsignalrepresent
thenodesareofline.(FromMislove,A.etal.2007.Measurementandanalysis
ofonlinesocialnetworks.In
Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM Conference
on Internet Measurement
[SanDiego,California,October24-26,2007].IMC
'
07.
ACM,NewYork,29-42.)
12.6.2 Transmissibility
Transmissibility
γ
denotes that the possibility that nodes x and y can contact each
other. If x is a carrier of the message, the message will be sent to y. In the ideal
model, transmissibility is assuming that all the nodes can always maintain contact.
However, realistically the transmissibility of the network depends on the status of
each node, which is online or offline.
Status: he status Pt denotes that one IM user at a given time in the set {Ponline,
Poline}. he status of a given node (active or inactive) can be assigned to either
{1,0}or {0,1}.
Origin: he origin is the message's source in the network.
Active Node: Active node is a user who is online at a given time t.
12.6.3 A graph of IM Network
he set V denotes all the IM network users or nodes. he set E represents the edges
between all the nodes. In the beginning, a selected node Vb is assumed as the mes-
sage carrier. Vb is referred to the origin of the IM network. A neighbor node Vc
is in the set A. he possibility of the joint between the node Vb and Vc, p(c
∩
b),
denotes that the message is transmitted from the origin Vb to Vc. he probability
of the joint for nodes b and c is: p(c
∩
b) = p(b).p(c). Figure 4 illustrates an IM evo-
lution procedure.
12.6.4 The General Information Dissemination Model
To better calculate the number of nodes to which the message can be delivered at
a given time t, we may define the term reachability to measure it as the set R. In
the ideal case, we presume that the transmissibility and susceptibility are equal to
one. he paths for the message transmission in the IM network are equal to the
radius of the network. At time t, the set R is equal to set A because the possibility