what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
final act of a ship operator's error. Rasmussen's [4] accident analysis of oil tankers
and ferryboats brought the interactions between these parties associated with the
Maritime Transport System to light [6,7,8], which supports the idea of considering
other factors beyond human error into the systematic approach of risk analysis.
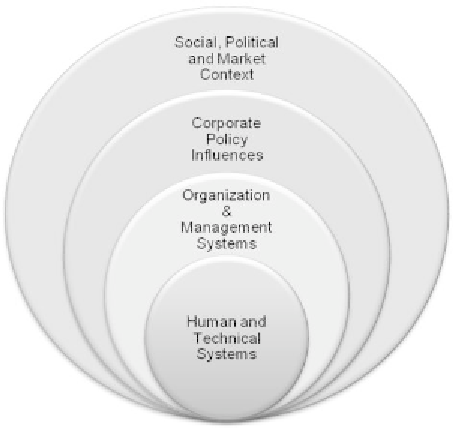
he International Maritime Organization (IMO) used Regulatory Influence
Diagrams (RID) [9] as a systematic approach to access risks for shipping activity.
he RID is used to achieve a better understanding of all influencing factors and
how they related to possible accidents. Figure 9.3 illustrates the structure of a RID.
he RID serves as a basis for establishing the contribution of relevant factors for all
system levels. It identifies the hierarchy of factors at every level that contribute to
possible accidents. Each factor is an idea for improvement. Upon identification of
all factors, each can be further analyzed to determine the best route to take in order
to achieve the necessary improvements.
A Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) is a probabilistic model used to represent a
set of random variables and their conditional independences via a directed acyclic
graph (DAG) [11]. he Bayesian Belief Network directly correlates to an inluence
diagram in which the effects of the represented factors are in terms of conditional
probabilities. his idea can be extended to encompass the relationship between con-
sidered factors and how they relate to possible accidents occurring in the Maritime
Transport System.
Figure9.3
NestedsystemofinluencesinaRegulatoryInluenceDiagram.(From
International Maritime Organization (IMO), Guidelines for the application of
FormalSafetyAssessment(FSA)foruseintheIMOrule-makingprocess,Publisher:
IMO.London,England,April2002.