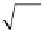what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
to others and others have the same perception to them. In this case, these two per-
spective models are structural equivalent. Structural equivalence is defined as:
Definition.1:
: Perspective models
ρ
i
C
f
and
ρ
C
f
toward a objective
C
f
are structur-
ally equivalent if the relation
x
ki
=
x
kj
and
x
ik
=
x
jk
for
k
=
1,2,...,
g
.
Since structural equivalence is a mathematical property, which is seldom actu-
ally realized in collected perspective data, we use Euclidean distance as a measure-
ment of structural equivalence. Different from the
d
i j
,
defined in the intuitive
approach, the Euclidean distance quantifies the similarity of the perspective models
based on the analysis of stakeholders' responses to each other.
Definition.2:
For perspectives
ρ
i
C
f
and
ρ
C
f
,
d
i,j
is the distance between rows
i
and
j
, and columns
i
and
j
of the perspective interaction matrix:
g
∑
=
⎣
−
+
−
⎦
d
(
x
x
)
2
(
x
x
)
2
i j
,
ik
jk
ki
kj
=
k
1
=
/2 2
If
ρ
i
C
f
and
ρ
C
f
are structurally equivalent, then the Euclidean distance between
them will be equal to 0.
If we want to compare stakeholders' perspective models for one argument
against more than one objective, we can generalize the above equation to measure
structural equivalence across the collection of several perspective models (i.e., a
perspective model set).
he normalized distance is
d
'
d
g
.
i j
,
i j
,
C
C
C
R
C
C
C
R
Definition.3:
For perspective sets
{
ρ ρ ρ
i
,
,...,
}
and
{
ρ ρ ρ
j
,
,...,
}
for objec-
1
2
1
2
i
i
j
j
tives
C
1
,...,
,
x
ijr
is the perception relation from stakeholder
i
to stakeholder
j
on objective
C
r
. he value of
d
i j
,
is the distance between the perceptions from and
to stakeholder
i
and
j
across the collection of
R
relations:
C
R
g
R
∑
∑
=
⎣
−
+
−
⎦
d
(
x
x
)
2
(
x
x
)
2
i j
,
ikr
jkr
kir
kjr
=
=
r
1
k
1
=
/2 2
here exist different measures of structural equivalence. Euclidean distance
and correlation are two typical methods in measuring positional structural equiva-
lence. Correlation is preferred in measuring the pattern of perceptions between two
perspectives (i.e., two stakeholders' opinions). Euclidean distance is preferred in
measuring the identity of the perspective relations. In our perspective model com-
parison, we use Euclidean distance since the purpose is to determine the similarity
he normalized distance is
d
'
d
Rg
.
i j
i j
,