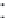what-when-how
In Depth Tutorials and Information
6.3.3.1 Connectivity Matrix
To compare with the results from previous papers [29,4], we present the connec-
tivity matrix of peer connections during the experiment. he connectivity matrix
is a scatter plot, where a point at location (
i
,
j
) in the plot refers to the fact that
peer
i
is connected to peer
j
. he peer index
i
is created by sorting the peers by
their joining time.
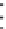
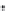
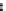
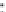
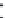
Figure 6.18 shows the connectivity matrix formed after 4 hours at the end of
the startup stage when most of the peers have joined the torrent. he fan-out shape
from the lower left to upper right corner of the matrix occurs due to the early peers
filling their 80-neighbor limit and refusing later connections, and is very similar
to previous results [4] shown in Figure 6.19. However, there is some additional
connectivity between early and late peers, which is due to some of the early peers
being the fastest downloaders and having already completed their downloads. Once
they become seeds they disconnect from other seeds in the system, thus freeing up
neighbor slots for later peers. he previous results shown in Figure 6.19 were taken
before any peers became seeds, and so do not show this feature.
Although Figure 6.18 does match well with the previous results at the early
stages of the experiment, we now proceed further into the experiment to see how
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
Peer Index
Figure6.18
Theconnectivitymatrixathour4.