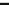
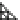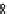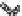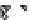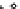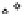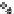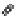Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
Veh
200
Des
Flu
150
**
#
**
100
***
50
***
0
+/+
+/-
-/-
b
Veh
Acute Rol
Repeated Rol
200
150
100
*#
50
0
-/-
+/+
+/-
Genotypes
Fig. 4 Effects of antidepressants on immobility duration in the forced swim test in the PDE4D
þ
/
þ
,
PDE4D
mice. (a) The effect of desipramine (Des) or fluoxetine (Flu). (b)
The effect of acute or repeated treatment with rolipram (Rol, 0.5 mg/kg). All the drugs or vehicles
[Veh; saline in (a) and 10% DMSO in (b)] were administered 30 min before the test. For the test
involving repeated treatment with rolipram, the drug was administered once daily for 8 days; the
forced swim test was conducted 30 min after the last injection (i.e., on day eight). Values shown
are mean
þ
/
, and PDE4D
/
SEM;
*
p
0.05,
**
p
0.01,
***
p
0.001 vs. corresponding genotype administered
<
<
<
vehicle (Veh);
#
p
0.05 vs. PDE4D
þ
/
þ
following the same treatment (
n
¼
5-7). Reprinted with
<
permission from (Zhang et al.
2002a
)
rules and procedures that are specific to a given situation and which remain valid
each time the situation is encountered (Olton
1983
; Cassel et al.
1998
). Scopol-
amine, a muscarinic cholinergic receptor antagonist, has been used to induce
impairment of working and reference memory. Rolipram reverses scopolamine-
induced deficits in both working memory and reference memory in the radial-arm
maze test (Zhang and O'Donnell
2000
).
Contextual fear memory can be tested in a paradigm of fear renewal that is
a model to study the interplay of context and memory retrieval. In this paradigm,
a change of context after extinction results in robust return of the conditioned fear
response. The renewed expression of fear demonstrates that extinction memory
is gated by contextual information (Bouton et al.
2006
). Recent studies suggest
that rolipram enhances long-term memory formation in the conditioned fear res-
ponse test (Mueller et al.
2010
). Understanding the neurobehavioral mechanisms