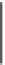Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Basement Membrane
Ca
2+
α
-Dg
SKELETAL
MUSCLE
biglycan
sarcoglycans
AChR
DGC
δ
β
α
γ
SPN
T-Tubule
Ca
2+
Golgi
Complex
dystrophin
dystrobrevin
Ca
2+
α
-syn
α
-syn
PKG
sGC
γ
-actin
DHPR
nNOS
β
nNOS
μ
nNOS
μ
Ca
2+
GTP
CaM
cGMP
5'GMP
CaM
caveola
L-Arg
ON-S
RyR1
NO
L-Arg
PDE5
NO
L-Arg
NO
Cav-3
Ca
2+
sarcomere
nNOS
μ
α
-syn
Ca
2+
SR
CaM
nNOS
μ
RyR1
Ca
2+
L-Arg
sarcolemma
NO
Basement Membrane
α
-Dg
sarcoglycans
Ca
2+
SMOOTH
MUSCLE
Ca
2+
SPN
ζ
δ
εβγ
caveola
Hypoxia
dystrophin
Cav-1
NO
pO
2
syn
Ca
2+
syn
nNOS
Ca
2+
Ca
2+
CaM
NO
nNOS
L-Arg
RyR
sGC
L-Arg
Ca
2+
NO
GTP
cGMP
PKG
IRAG
GTP
PDE5
RGS2
pGC
SR
5'GMP
muscle contractility
cGMP
MLCP
Ca
2+
Basement Membrane
α
-Dg
sarcoglycans
CARDIAC
MUSCLE
β
α
γ
δ
SPN
Ca
2+
T-Tubule
dystrophin
dystrobrevin
nNOS
μ
α
-syn
α
-syn
GTP
pGC
Cav-3
Cav-3
eNOS
eNOS
cGMP
L-Arg
sGC
LTCC
Ca
2+
NO
Ca
2+
Ca
2+
GTP
cGMP
L-Arg
PKG
sarcomere
CaM
PDE1c
PDE5?
nNOS
μ
RyR
S-NO
nNOS
μ
CaM
Ca
2+
RyR
5'GMP
SR
Ca
2+
SR
nNOS
μ
CaM
Fig. 1 Propagation of NO-cGMP signals in skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Nitric oxide
synthase enzymes (nNOS and eNOS) regulate, and are regulated by, Ca
2+
fluxes in muscle
cells. Ca
2+
/CaM activation of nNOS (or eNOS) leads to synthesis of NO, which in turn
binds and activates sGC. cGMP produced by sGC then modulates downstream effector activity
(see text) Abbreviations:
a
-Dg,
a
-dystroglycan;
b
-Dg,
b
-dystroglycan;
a
-syn,
a
-syntrophin;
AChR, nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; CaM, calmodulin; Cav-1, Caveolin-1; Cav-3, caveolin-3;
DHPR, dihyropyridine receptor; IRAG, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor I-associated cGMP