Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
500
50
400
30
300
200
10
100
550
600
650
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Elution time (s)
Time (min)
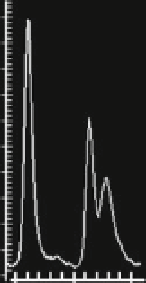
Fig. 6 Establishment of a capillary electrophoresis phosphodiesterase assay. (a) Raw data of an
hPDE 5 assay with 200 nM fluorescein-tagged cGMP as a substrate as detected by capillary
electrophoresis using a 12 sipper chip and the Labchip 3000 reader (Caliper Life Sciences;
conditions: upstream voltage -250 V, downstream voltage -2,500 V, - 2.7 bar). Shown is the
elution profile of one sipper (two sips) with a negative control eluting between 550 and 600 s and a
positive sample with cGMP and GMP eluting between 600 and 650 s. To analyze a 384-well plate,
each of the 12 sippers takes in 32 sips in a defined geometric fashion. Substrate and product peaks
are automatically assigned to individual wells, and percent turnover is calculated from the relative
peak heights of substrate and product. (b) Time course of the hPDE5 capillary electrophoresis
assay using 200 nM fluorescein-tagged cGMP as a substrate to determine a suitable enzyme
amount for retesting with native PDE5 from platelet cytosol (quadruplicates). Note the excellent
reproducibility of the assay as evident by the minute
error bars
. In the screen, cGMP turnover was
adjusted to 35% (90 min, 20
C) by adding a suitable amount of enzyme protein
The assays were carried out on the robotic system in 384-well plates. Within
40
m
l, the samples comprised 2.4% DMSO, 20 mM HEPES, 0.01% Tween 20,
0.01% BSA, 1 mMMgCl
2
,10
m
M of the PDE3 inhibitor Motapizone, 100 nM of the
PDE2 inhibitor Bay 60-7550, and 0.2, 5, or 20
m
M cGMP. The reaction was stopped
by the robot with 40
m
l of stop buffer (100 mM HEPES, 5% DMSO, 1% coating
reagent from Caliper Life Sciences, 5 mM EDTA, pH 7.4). Then the plates were
transferred to the Labchip 300 capillary electrophoresis reader (Caliper Life
sciences) and detection was carried out automatically overnight, thus opening up
this method to medium throughput. The assay was validated by means of a
concentration-response curve for the established PDE5 inhibitor sildenafil (logIC
50
¼
8.2 when assayed with 200 nM fluorescein-tagged cGMP as substrate; Fig.
7c
).
Sixty-seven compounds were assayed at three cGMP concentrations (see above).
Fourteen compounds inhibited hPDE5 activity better or equally good at 20
m
M
compared to 200 nM cGMP. This indicates that these compounds inhibited both
activation via GAF domain and the catalytic site of PDE5. NYC175273, an inhibi-
tor of PDE5-GAF-CyaB1 (Fig.
7c
), is shown as a representative example for this
group of compounds (Fig.
7d
). Two further compounds inhibited exclusively at
higher cGMP concentrations. We assume that they act as allosteric inhibitors at the
GAF domain, while the catalytic site of PDE5 remains unaffected.