Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
6 Binding of the Products Does Not Simulate Binding
of the Substrates
The glutamine switch mechanism is based on the assumption that the products
simulate the binding of the substrates because they share the nucleoside portions.
However, since products of enzymatic reactions serve as leaving groups and often
have much lower affinity than substrates, significant differences in binding of
substrates and products are expected and therefore the suitability of the model is
in question. To this purpose, the structure of a PDE4D2 mutant in complex with
cAMP was determined at high resolution (Wang et al.
2007b
). The superposition of
PDE4D2-cAMP over PDE4D2-AMP (Huai et al.
2003
) yielded the small RMSD of
0.26
˚
, indicating overall similarity of the protein structures. In addition, cAMP and
5
0
-AMP have the same
anti
configuration and interact with a similar set of amino
acids (Fig.
4
). However, the hydrogen bonding patterns of cAMP and 5
0
-AMP in the
structures of PDE4D2-cAMP and PDE4D2-AMP are very different (Fig.
4a
). First,
a phosphate oxygen of 5
0
-AMP bridges the two divalent metal ions, but cAMP does
not directly contact the metal ions. Second, the side chain of Asn321 in the
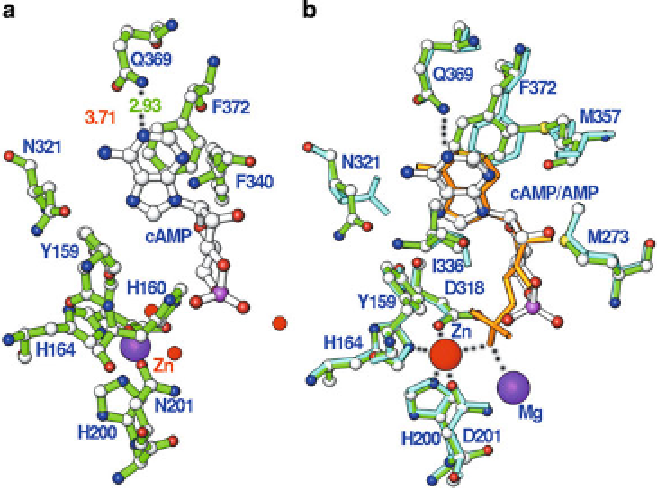
Fig. 4 Binding of substrate cAMP and product 5
0
-AMP in the PDE4D2 structures. (a) Binding of
cAMP to the pocket of PDE4D2. Gln369 forms only one hydrogen bond (
dotted line
) with cAMP.
(b) Superposition of cAMP (
white bonds
) over 5
0
-AMP (
golden
bonds). The
green
colored bonds
represent residues from the PDE4D2-cAMP structures, while cyan is for residues of PDE4D2-
AMP. The side chain conformation of Asn321 is different in the two structures. Phe372 shows
some positional changes while other residues have no significant difference