Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
100
40
Fe
Cr
Ni
O
90
35
80
30
70
25
60
50
20
40
15
30
10
20
5
10
0
0
0
50
100
Position (nm)
150
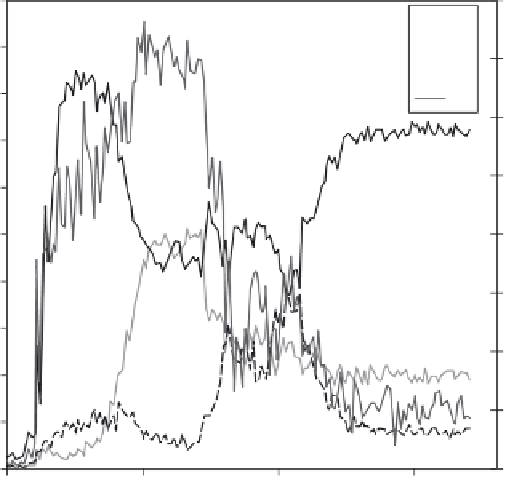
2.1
EDX profi le on 304 L exposed to water (360°C, pH
325°C
= 7.2).
Finally, passivation is the process of building a protective layer of oxide isolating
the surface of the material from the aggressive environment. Some corrosion
inhibitors help the formation of such layers. Figure 2.1 shows energy-dispersive
x-ray (EDX) analysis of the oxide formed on stainless steel exposed to water
at 360°C (−600 mV
SHE
, pH
325
°
C
= 7.2). The passive fi lm is the 50 nm-thick layer
containing a signifi cant level of chromium at the surface of the metal.
2.2
Pressurized water reactors and the main
types of corrosion
2.2.1 PWRs
A large variety of structural metals present in primary and secondary
circuits of PWRs suffer corrosion:
Carbon steels
are cheap iron-base metals with less than 1% of alloying
element present. These materials exhibit a poor resistance to corrosion
but their forming, machining and welding are superior.
Low-alloy steels
are iron-base metals containing a few percent of, for
example, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, which are usually


Search WWH ::

Custom Search