Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Agressive
environment:
Iodine
Tensile stress:
Power ramp
SCC
Sensitive material:
Zry-2, Zry-4
5.4
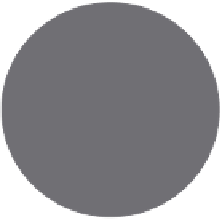
Schematic showing the three components involved in SCC
(Strasser
et al
., 2010a).
2.
The second remedy - design improvement - consists of two approaches:
2a. Cladding design
2a1. Development of radial cladding texture and small grain size
that may increase cladding PCI resistance.
2a2. Development of the barrier/liner concept, initially with a 'pure'
zirconium (Zr) metal barrier at the cladding inner diameter (ID).
The barrier is soft and serves to reduce the local stress, hence giv-
ing the cladding resistance to SCC. Later, fuel vendors realized
that the Zr could be alloyed with Fe to improve the secondary
degradation resistance in case of rod failure. The Fe in the Zr will
dramatically improve the corrosion resistance of the liner/barrier
but may reduce the PCI performance. Although this remedy has
so far only been used in BWRs, it should be equally applicable
to PWRs.
2b. Pellet design
2b1. Reducing the cladding local strains (and stresses) by shortening
the pellet, chamfering the corners and eliminating the dishing.
2b2. Pellets with additives are being developed both for BWRs
and PWRs that will increase the margins towards PCI failures
(Adamson
et al
., 2006/7; Patterson, 2010). The additives of inter-
est fall into two general categories, the fi rst category involves
materials that are essentially insoluble in the fl uorite lattice and
exists as a separate, grain boundary phase, for example, mix-
tures of alumina and silica (aluminosilicates or Al-Si-O). The
second category involves materials that are soluble in the cat-
ion sub-lattice, such as chromia, or involve a mixture of soluble
and insoluble materials, such as chromia and alumina. Although









Search WWH ::

Custom Search