Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
P
0
1.0
P
n
(t
0.5
P
6
P
6
0
-1.0
-0.5
0.5
1.0
P
4
-0.5
P
4
P
2
-1.0
t=cos
#
1.0
P
1
P
n
(t
P
3
0.5
P
5
P
7
0
-1.0
-0.5
0.5
1.0
P
7
P
5
-0.5
P
3
P
1
-1.0
t=cos
#
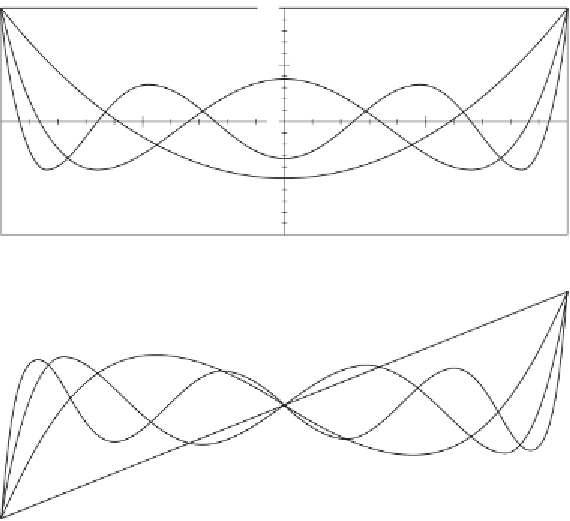
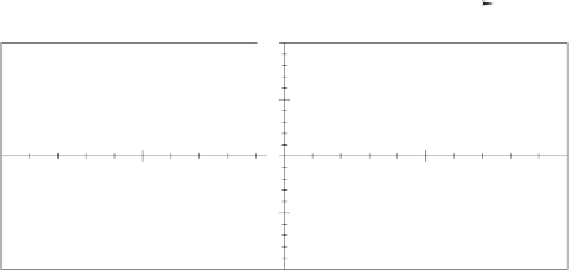
Fig. 1.4. Legendre's polynomials as functions of
t
=cos
ϑ
:
n
even (top)
and
n
odd (bottom)
If the order
m
is not zero - that is, for
m
=1
,
2
,...,n
- Legendre's functions
P
nm
(cos
ϑ
) are called
associated Legendre functions
. They can be reduced to
the Legendre polynomials by means of the equation
t
2
)
m/
2
d
m
P
n
(
t
)
dt
m
P
nm
(
t
)=(1
−
,
(1-65)
which follows from (1-57) and (1-59). Thus, the associated Legendre func-
tions are expressed in terms of the Legendre polynomials of the same degree
n
.Wegivesome
P
nm
,writing
t
=cos
ϑ
,
√
1
t
2
=sin
ϑ
:
−
P
31
(cos
ϑ
)=sin
ϑ
1
2
cos
2
ϑ −
2
,
3
P
11
(cos
ϑ
)=sin
ϑ,
(1-66)
P
21
(cos
ϑ
)=3sin
ϑ
cos
ϑ, P
32
(cos
ϑ
)=15sin
2
ϑ
cos
ϑ,
P
22
(cos
ϑ
)=3sin
2
ϑ,
P
33
(cos
ϑ
)=15sin
3
ϑ.
We also mention an explicit formula for any Legendre function (polynomial