Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
2.14
Gravity anomalies outside the earth
If a harmonic function
H
is given at the surface of the earth, then, as a
spherical approximation, the values of
H
outside the earth can be computed
by Poisson's integral formula (1-123)
r
2
R
2
R
4
π
−
H
P
=
Hdσ.
(2-274)
l
3
σ
The symbol
σ
is the usual abbreviation for an integral extended over the
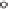
whole unit sphere. The meaning of the other notations is read from Fig. 2.14.
The value of the harmonic function at the variable surface element
R
2
dσ
is
denoted simply by
H
,whereas
H
P
refers to the fixed point
P
.Thenweget
l
=
r
2
+
R
2
−
2
Rr
cos
ψ.
(2-275)
The harmonic function
H
can be expanded into a series of spherical har-
monics:
H
=
R
r
H
0
+
R
r
2
R
r
n
+1
H
1
+
∞
H
n
.
(2-276)
n
=2
By omitting the terms of degrees one and zero, we get a new function
R
r
H
0
R
r
2
R
r
n
+1
H
1
=
∞
H
=
H
−
−
H
n
.
(2-277)
n
=2
P
r
l
Ã
Ã
R
2
¾
R
d
¾
unit sphere
r=1
terrestrial sphere
rR
=
Fig. 2.14. Notations for Poisson's integral and derived formulas