Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Homogeneous
70
300
200,000
100,000
10,000
200,000
10,000
60
250
50
200
40
150
30
100
20
10
50
0
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
0
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
Heterogeneous
300
70
200,000
10,000
200,000
100,000
10,000
60
250
50
200
40
150
30
100
20
50
10
0
0
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
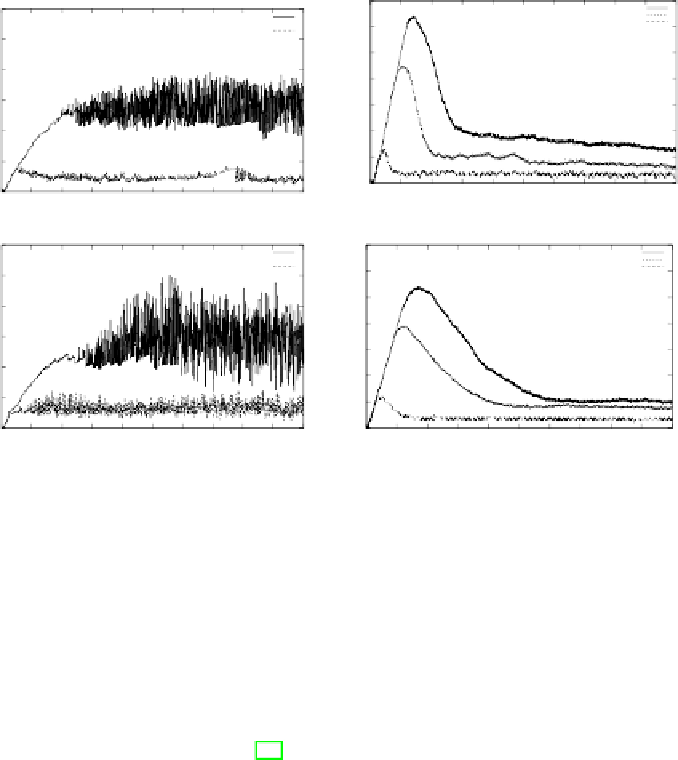
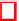
Fig. 3.
The graphs show of maximum cell degree vs time and average cell degree vs
time for homogeneous and heterogeneous networks for values of
u ∈
10
K,
100
K
and
200
K
. All experiments are run using the same seed value.
U
= 100
,
000 is omitted from
the maximum degree graph for clarity — points are joined by lines in these graphs to
indicate the trend.
5.3
Clustering Coecient
A clear indication that a network deviates from that of a random graph with an
equivalent number of vertices and edges can be obtained by examining the clus-
tering coecient of a network, which is expected to differ by a factor of order
n
(where
n
is the number of nodes) [15]. It has been observed experimentally that bi-
ological networks have high cluster coecient. However, table 1 shows that we find
the clustering coecients of the networks obtained with our model to be low in all
cases with no obvious trend as either
U
is increased or the network is evolved with
either heterogeneous or homogeneous types. This is not unexpected — due to the
complementary a
nity function used in the 2D space, a large number of cells are
physically unable to form clusters (i.e. if A recognises B, and B recognises C, then
C cannot recognise A for the majority of (
x, y
) coordinates. On the other hand,
some clustering does occur; the cluster coecients are markedly higher than those
found by [4] which produced clustering coecients of the order
<
10
−
5
.
5.4
Degree Distribution
Figure 3 provides evidence that natural hubs do exist in the network: the left-
hand plot shows that very high levels of connectivity are achieved by a few cells
in the network in comparison to the average degree of the network cells shown in