Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
5.1 System Overview
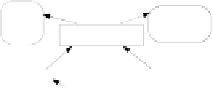
Figure 3 shows the overall architecture of the Danger Theory based AIS, which
employs the DC algorithm (DCA). Our Danger Theory based AIS comprises of two
stages: (i) Detecting misbehaving nodes and (ii) detecting antigens and responding to
the detected antigens. The DCA performs the first stage of the job, detecting
misbehaving nodes. The second stage of the job involves sending immune cells and
signals between the nodes of the sensor network. This may be performed by a
different immune inspired algorithm such as the one introduced in [11]. This paper
focuses on the first stage.
Sensor Node
DC Algorithm
Safe
Antigens
Dangerous
Antigens
DC Analyser
DC Maturation
Semi-Mature
DCs
Mature
DCs
Immature
DCs
Antigens
Signals
Antigens
Signals
Direct Diffusion
Antigen Extractor
Signal Generator
Interest Packets
Data Packets
Interest Cache
Data Cache
Fig. 3.
DC algorithm and Directed Diffusion execute on a sensor node
Interest Packets
Data Packets
A sensor node employing Directed Diffusion maintains two tables; the interest
cache and the data cache and handles two types of packets; interest packets and data
packets. While there are four possible sources of antigens and signals for input to the
DCA, namely: (i) The interest cache, (ii) the data cache, (iii) interest packets and (iv)
data packets. The signal generator and an antigen extractor are implemented as a sub-
module of Directed Diffusion, thereby integrating the AIS into the protocol. When a
packet arrives at a node, Directed Diffusion updates the interest and/or a data cache
according to its local cache update rules [9], and extracts the signals and antigens
from the packet(s) and/or cache(s). These are then passed to the DCA.
The immature DCs of the DCA sample the antigens and store them in their internal
storage. They also combine various input signals using the signal weighting function
shown in equation (1). The evaluation of the input signals results in output cytokines
that differentiate between the immature DCs, to either become semi-mature or mature
DCs. Antigens contained in semi-mature DCs are regarded as being collected under a
normal condition, in contrast to the antigens stored by mature DCs that are collected
under attack conditions. The DC analyser of the DCA reviews all the antigens stored
in semi-mature and mature DCs and determines the state of each antigen as either
“benign” or “malicious”.