Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The most important factors that should be regarded for the control of the heating
system are the outdoor temperature, indoor temperature, type of the room, frequency
of use, daytime, weekday, and ventilation. For the outdoor temperature an air
temperature sensor must be installed outside the home. The indoor temperature is
measured by air temperature sensors in each room. The temperature should be on a
level that is pleasant to the inhabitants. Here, feedback can be given by the inhabitants
by adjusting the temperature. The type of the room and the frequency of use are
closely related. The frequency can be measured by motion detectors in the rooms. It
clearly varies according to the type of the room but also to the daytime and even to
the weekday. Daytime and weekday are in general important for the temperature, e.g.
during the night, the temperature can be reduced. Ventilation also plays a role because
a well controlled ventilation produces a good indoor climate and saves energy.
3 The Structure and Functioning of the AIS
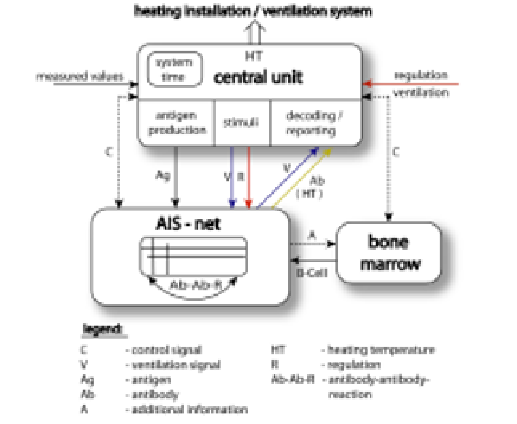
The architecture of the AIS for the heating system is shown in figure 2. It consists of
three components: the central unit, the AIS-network and the bone marrow. The central
unit serves as an interface to the outside world, i.e. to the hardware of the heating
system. It receives signals and produces antigens from these signals, and in the
opposite direction it transforms the output of the network into commands to the
heating system. The bone marrow produces new B-cells and adapts them to the needs
of the AIS-network if necessary. The AIS-network performs reactions to the
stimulations by antigens and antibodies by the operations selection and mutation, both
based on the affinity between the elements.
Fig. 2.
The architecture of the AIS