Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.1 Fuzzy resource allocation mechanism
The competition of resources in AIRS allows high-affinity ARBs to improve. Accord-
ing to this resource allocation mechanism, half of resources are allocated to the ARBs
in the class of Antigen while the remaining half is distributed to the other classes. The
distribution of resources is done according to a number that is found by multiplying
stimulation rate with clonal rate. In the study of Baurav Marwah and Lois Boggess, a
different resource allocation mechanism was tried [13]. In their mechanism, the Ag
classes occurring more frequently get more resources. Both in classical AIRS and the
study of Marwah and Boggess, resource allocation is done linearly with affinities.
This linearity requires excess resource usage in the system, which results long classi-
fication time and high number of memory cells.
In this study, to get rid of this problem, resource allocation mechanism was done
with fuzzy-logic. So there existed a non-linearity because of fuzzy-rules. The differ-
ence in resource number between high-affinity ARBs and low-affinity ARBs is bigger
in this method than in classical approach.
The input variable of Fuzzy resource allocation mechanism is stimulation level of
ARB hence the output variable is the number of resources, which will be allocated to
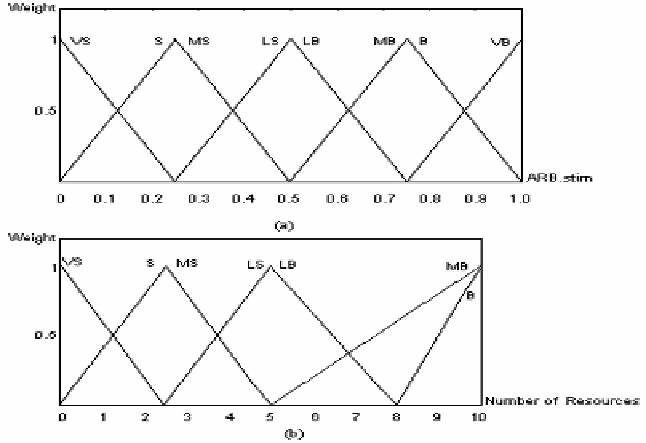
that ARB. As for the other fuzzy-systems, input membership functions as well as
output membership functions were formed. The input membership functions are
shown in Fig. 2.a.
Fig. 2. a) Input membership function, b) Output membership function
The input variable, ARB.stim, varies between 0 and 1. A membership value is cal-
culated according to this value using input membership functions. In this calculation,
two points are get which are the cutting points of membership triangles by the input