Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
motivating hypothesis, the different anities for the stimulation and the reg-
ulatory cytokine for the effector cells plays an important role in this model.
Therefore, the constants involved in this step have great influence on the model,
because the cell activation level is used as a measure of the response magnitude.
Given the cytokine inputs, the resultant input is then determined, according
to 5, where
k
r
and
k
s
are positive values, named regulation and stimulation
constants, respectively.
ψ
i
stimulation
−
ψ
i
regulation
χ
=
k
s
·
k
r
·
(5)
Effector Cells.
Closer inspection of equation 5 reveals that the resultant input,
when negative, implies that cell regulation exert domination over cell stimula-
tion, and the cell activation level should be decreased. On the other hand, a
positive resultant input should increase the activation level. To model the acti-
vation level update process, the sigmoid function is used. The new cell activation
level, given as a function of the resultant input and current activation level, is
given by equation 6, where
α
0
is the current activation level,
χ
is the resultant
input and
σ
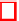
is the sigmoid function steepness. To illustrate the activation func-
tion, it is shown in figure 3, as a function of the resultant input (
χ
), for two
values of
α
0
and
σ
(
α
0
=0
.
2
,σ
=0
.
1and
α
0
=0
.
8
,σ
=0
.
2).
1
α
(
χ, α
0
)=
(6)
1+
1
−α
0
α
0
·
exp
(
−
σ
·
χ
)
Fig. 3.
Plots of the new cell activation level as a function of resultant input for
α
0
=
0
.
2
,σ
=0
.
1and
α
0
=0
.
8
,σ
=0
.
2
The activation function shown in figure 3 has two interesting characteristics:
-
the current activation level (
α
0
in equation 6) is related to the horizontal
translation of the activation curve. As a matter of fact, the curve is trans-
lated so that
α
(
χ
=0
,α
0
)=
α
0
; thus, in the absense of input stimuli, the cell