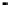Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
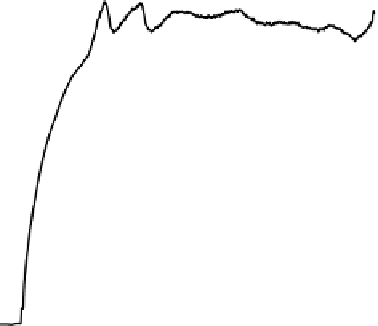
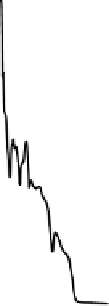
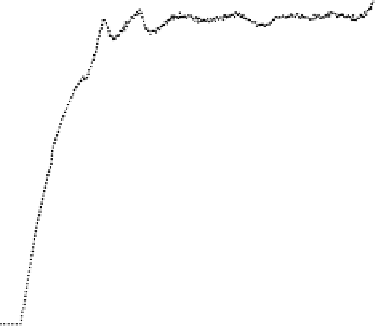
Subsequent inspection of the bed indicated a substantial volume of agglomerated sand
particles. Once the bed began to clinker, the fuel feed was switched off so that the bed
temperature decreased. The subsequent recovery in bed pressure as shown in the figure is
probably due to solidification of the sticky deposits and partial breakup of the weak brittle
bonds between sand particles by the air.
1000
400
900
350
800
300
700
250
600
500
200
400
Bed temperature
Freeboard temperature
Bed pressure
150
300
100
200
50
100
Raffinate on
0
0
0.00
0.50
1.00
1.50
2.00
2.50
Time (hr)
Figure 9. Bed behaviour during co-combustion of coal and raffinate.
Table 17. Test conditions for Coal-Raffinate test
Coal flow for 81 min (kg/h)
2.8
Coal flow for 81 min (kW)
23.3
Coal flow for 7 min (kg/h)
3.2
Coal flow for 7 min (kW)
26.7
Raffinate flow (l/h)
2.88
Raffinate flow (kg/h), Density = 1320 kg/m
3
3.8
Coal to Raffinate feed ratio (kg/h)/(kg/h)
0.84
Coal (%)
45.7
Raffinate (%)
54.3
Coal only feed time (hrs)
0.9
(Coal + Raffinate) feed time (hrs)
0.57
Total coal feed time (hrs)
1.47
Total coal feed (kg)
4.22
Total reffinate feed (kg)
2.2
Coal to raffinate mass ratio (kg/kg)*
1.92
Sand to raffinate ratio (kg/kg)*
3.4
*Ratio of total material fed to the bed