Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
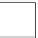
(B
ij
is the element in row
i
, column
j
)
(1)
B
ij
Row
i
i
th coefficient of
f
(
s
,
v
)
SH expanded using the view vector
v
(Coefficient
y
i
(
v
))
Column
j
(2)
j
th coefficient of the SH expansion of (1)
using incident light as a variable = B
ij
(2)
(Coefficient
y
i
(
s
)) (element in row
i
, column
j
)
Figure 10.8
BRDF matrix.
i
is a function of the viewing direction
v
, i.e., is a function on the sphere, and can
therefore be approximated by an expansion in spherical harmonics. Coefficient
j
of the SH expansion of
b
i
is denoted by
b
ij
; these coefficients collectively form
a
BRDF matrix
(
Figure 10.8
).
The construction of a BRDF matrix is similar to the construction of a transfer
matrix described in Section 10.1.2. The SH coefficient
b
i
(
v
)
(
)
(
,
)
v
of the function
b
s
v
is computed from projecting
b
(
s
,
v
)
onto the SH basis function of index
i
:
b
i
(
v
)=
b
(
s
,
v
)
y
i
(
s
)
d
s
Ω
4π
and coefficient
j
of the SH expansion of
b
i
(
v
)
is
=
(
)
(
)
=
(
,
)
(
)
(
)
b
ij
b
i
v
y
j
v
d
v
b
s
v
y
i
s
y
j
v
d
sd
v
(10.9)
Ω
4π
Ω
4π
Ω
4π
Rows of a BRDF matrix correspond to the variation in the viewing direction;
columns of a BRDF matrix correspond to the variation in the light direction.
The BRDF matrix as defined in Equation (10.9) predates PRT by a full decade,
having been introduced in 1992 by Stephen H. Westin, James Arvo, and Ken-
neth E. Torrance in the paper “Predicting Reflectance Functions from Complex
Surfaces” [Westin et al. 92]. This work was concerned with photorealistic ren-
dering of surfaces having complex mesostructure, and it succeeded—the paper
contains some of the most realistic (synthetically generated) surface renderings
ever produced. The application of spherical harmonics by Westin et al. in 1992
had a substantial impact on PRT research in the following decade. Equation (10.9)
is very similar to the construction of the transfer matrix given in Equation (10.6).
In fact, a transfer matrix is a kind of generalization of a BRDF matrix: both trans-
form an incident light vector (a vector of SH coefficients) to an outgoing light