Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
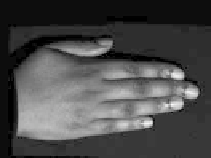
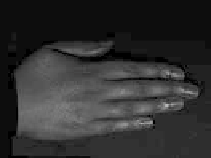
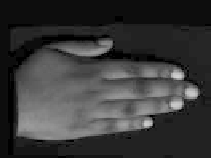
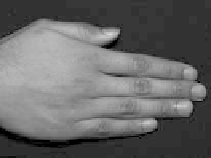
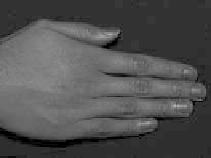
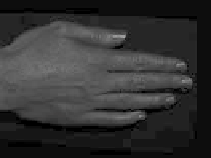
Figure 8.49
Separation of direct and indirect lighting in human hands. (a) Original captured image.
(b) Separated direct illumination. (c) Separated indirect light; most of this comes from
subsurface scattering. Evidently, subsurface scattering decreases with increasing skin pig-
mentation. (Courtesy of Shree K. Nayar, Columbia University.) (See Color Plate XII.)
as better surface reflection models, has expanded the idea of reflection to include
more global effects. Methods of separating a captured image into the effects of
direct illumination and the effects of global illumination will doubtlessly play an
important role in creating more globally oriented reflectance models.
8.4 Reflectance of Hair
This chapter has explored the development of general reflectance models. The
remainder of the chapter is devoted to the specific but very important problem of
rendering human hair. The demand for photorealistic rendering of hair has existed
since the earliest days of realistic CG rendering. Fundamental models of hair
and hair rendering were established in the early days in CG. However, rendering
hair is a computationally costly job because of the geometric complexity and the