Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
1
unlit voxels. Consequently, this second scattering effect can be separated in
the same way as the other GI effects.
−
α
Practical separation.
The separation of direct and global illumination is the-
oretically possible from the two captured images of the scene under checkerboard
illumination described above. But complications arise in reality: digitally cap-
tured photographs have noise, and the projector does not produce a perfectly uni-
form radiance. These cause variation in the captured image pixel values that have
nothing to do with global illumination. To solve this, a set of images is captured
for each configuration by shifting the checkerboard pattern by small steps in each
direction. Normally five steps are used, so there are 25 images captured in to-
tal. Instead of manually selecting the lit and unlit pixels in the image,
L
+
[
c
,
i
]
and
L
−
[
are approximated from the largest and smallest corresponding pixel
values, respectively, in the 25 captured images (
Figure 8.43
)
.
Figure 8.44 shows some results of the separation method. The scene was con-
structed to include most of the global illumination effects considered in the paper.
The bright area in the corner where the two walls meet is a result of diffuse in-
terreflection. Specular interreflection occurs on the shiny object just under the
curtain. The slab of marble at the bottom center of the scene exhibits significant
subsurface scattering, as does the candle just behind it. The frosted glass container
at the right has a translucent surface, and the glass at the left contains diluted milk
that exhibits volumetric scattering. The scene in the bottom row is much simpler
in content, but has trickier high frequency reflection. Figure 8.44(a) contain an
c
,
i
]
L
max
L
+
=
L
max
Largest value
Direct illumination
Captured images
Smallest value
Global illumination
L
-
=
L
min
L
min
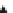
Figure 8.43
Separation using a checkerboard illumination pattern. A set of images are captured with
slight shifts in the checkerboard pattern (left). The maximum value of a pixel in the set of
images, denoted by
L
max
,servesas
L
+
. The minimum value serves as
L
−
. (From [Nayar
et al. 06] c
2006 ACM, Inc. Included here by permission.)