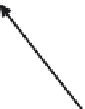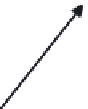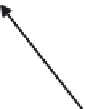Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
→
→
→
n
n
h
→
→
→
→
ω
ω
ω
ω
i
i
o
o
θ
h
θ
d
φ
d
θ
i
θ
o
→
→
x
φ
o
φ
h
φ
i
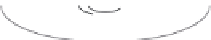
Figure 8.17
Parameterization used in image-based BRDFs. (From [Matusik et al. 03] c
2003 ACM,
Inc. Included here by permission.)
per employs an alternative parameterization proposed by Szymon Rusinkiewicz
[Rusinkiewicz 98]
(
Figure 8.17
)
. This parameterization uses the half-angle
θ
h
,
and measures the deviation of ω
i
from the half-vector with two parameters
θ
d
and
φ
d
. Specular reflection normally occurs when the half-angle is nearly
zero, so the samples can be concentrated near
θ
h
=
0. Sample points are taken at
1
◦
intervals over
φ
d
, and 90 nonuniformly spaced values of the half-angle
θ
h
most densely spaced near
θ
d
and
0. The authors acquired BRDF measurements
for a wide variety of surfaces. They started with 130 surface samples, but they
ended up using only 103 after they excluded those that exhibited anisotropy or a
notable positional dependence.
The approach taken in the paper was to regard all isotropic BRDFs as an
abstract space; elements of this space are individual BRDFs. The idea was to find
a general basis for this space. Because so many BRDF models depend on just
a few parameters, it seemed reasonable to conclude that all observable BRDFs
were part of a small subset of the full hypothetical BRDF space. A BRDF is
represented as a vector of sample values, or the logarithm of the values. In the
particular representation they employed, each sample has three color channels, so
the vector representing a particular BRDF has 3
θ
h
=
360 coordinates. The
natural basis for this vector space has as many basis elements, so it is not very
useful for a BRDF representation. A more representative basis was needed.
The
response matrix
is formed by placing the 103 measurement vectors in
the rows of a matrix (
Figure 8.18
). The rows of the response matrix represent
the variation in materials; the columns represent variation in the incoming and
outgoing directions. This response matrix thus contains the reflectance for the
discrete set of 103 samples. There are several techniques for approximating a
response matrix as a linear combination of basis vectors. One such method known
as
principal component analysis
(PCA) uses vectors of an associated matrix for
the basis elements. PCA uses eigenvector analysis. Eigenvectors correspond to
a set of representative incoming/outgoing direction pairs, and the most important
×
90
×
90
×