Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
x
x
= 0
x
= 1
x
= 2
Sensor plane
Microlens image
y
=0
u
x
y
=1
y
=2
y
v
y
Sub-aperture image
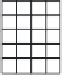
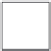
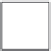
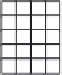
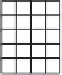
Figure 5.24
A subaperture image. A pixel (shaded) in a microlens image corresponds to what is seen
through a small virtual aperture on the lens. Collecting the corresponding pixel in each
microimage, which sees the same virtual aperture, produces a subaperture image. The
image is smaller than the sensor image, as there is only one pixel for each microlens.
depend on the sampling rate of the light field. In particular the refocusing sharp-
ness and the range of possible refocusing depths are linearly proportional to the
directional resolution. However, the method depends on a number of approximat-
ing assumptions, and the lack of a reference solution made it difficult to quantify
the accuracy of the light field and the error in the rendered images.
Fourier slice photography.
Ng developed a mathematical framework for light
field presented in the paper “Fourier Slice Photography” that provided a theoret-
ical foundation for light field imaging [Ng 05]. The main result of the paper is a
theorem called the
Fourier slice photography theorem
, which provides a method
for creating images from a light field in the Fourier domain. The theorem is based
on a generalization of a known theorem, the
Fourier slice theorem
that relates two
kinds of dimensional reductions of functions. To make this more precise, sup-
pose
F
is a real-valued function of
n
real variables. An
integral projection
of
F
is
obtained by integrating
F
over some of its variables, which results in a function
of
m
variables. For example, the integral in Equation (5.7) that determines the
irradiance at a sensor pixel is an integral projection:
L
F
(
E
F
(
x
,
y
)=
x
,
y
,
u
,
v
)
dudv
(5.10)
(this is one reason the cos
4
factor and the aperture functions are omitted or
absorbed into
L
F
). A
slice
is another kind of dimensional reduction obtained by
fixing some of the variables of a multivariate function. An example of a slice of
a function is the radiance distribution
L
F
(
θ
x
m
,
y
m
,
u
,
v
)
of the image of a microlens
at
(
x
m
,
y
m
)
. The Fourier slice theorem states that the Fourier transform of an