Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Q
P
Actual model
Approximately
recovered model
Epipolar plane
Key/warped
offset image
epipolar lines
Offset image
p
k
p
0
q
k
e
0
e
k
Offset
Key camera
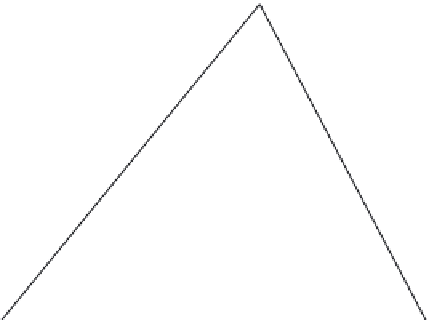
Figure 5.13
Pixel correspondence is determined in model-based stereo by searching the warped offset
image along the epipolar line in the key image. (After [Debevec et al. 96].)
used for the key image, and that used for the offset image. A point
P
in the scene
is contained in a unique epipolar plane through the two viewpoints. Suppose
p
k
is the pixel in the key image corresponding to
P
. Normally the pixel
p
o
corre-
sponding to
p
k
in the offset image is found by searched along the epipolar line
(the intersection of the epipolar plane through
P
and the image plane of the offset
image). In model-based stereo, however, the corresponding pixel is contained in
the warped offset image, which is formed by projecting the offset image onto the
model from the position of the offset camera (
P
is projected onto
Q
in
Figure 5.13
)
and that image is then projected back to the image plane of the key image. The
pixel
q
k
that corresponds to
p
k
therefore lies in on the epipolar line in the warped
offset image, which is the same as that of the key image.
The final rendering is performed by image warping. The recovery of the full
3D model and view-dependent texture mapping are performed before the final
rendering in order to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of rendering. However,
it is pointed out that these processes by themselves are not sufficient to create
an image that looks accurate. Possibly because of this, the process of recover-
ing a 3D model from photographs and then performing rendering after mapping
the captured images, which were used for the recovery, became the definition of
image-based modeling and rendering.