Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
u
v
(a)
(b)
w
x
v
v
(c)
(d)
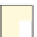
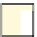
Fig. 1.
(a) A polyomino
P
of 16 cells with a hole of two cells. (b) Two points
v
and
u
are
r
-visible. (c)
v
and
x
are not
r
-visible. (d)
v
and
w
are not
r
-visible.
known that the same problem for simple orthogonal polygons is polynomial-time
solvable [
14
].
The research on the art gallery problem for polyominoes was firstly reported
in [
2
], where it was shown that
(
m
+1)
/
3
guards are always sucient and
sometimes necessary to cover an
m
-polyomino (possibly with holes). Here, an
m
-
polyomino is a connected polyomino consisting of
m
unit squares. Interestingly,
their
(
m
+1)
/
3
-bounds hold for three models of visibility:
r
-visibility model,
all-or-nothing model, and unrestricted model (see Fig.
2
).
(c)
(a)
(b)
Fig. 2.
(a)
r
-visibility model. (b) all-or-nothing model. (c) unrestricted model.
-visibility model is a subset of the
region visible from the same point in the all-or-nothing model (see Fig.
2
), which
is in turn a subset of that in the unrestricted model. Due to this property, the
proof of the NP-hard result for orthogonal polygons in the unrestricted model
in [
8
] does not hold in the
The region visible from a point in the
r
-visibility model. In the conference version [
1
]ofthe
above paper [
2
], the NP-hardness was shown for all-or-nothing and unrestricted
models.
r





























































































































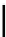












Search WWH ::

Custom Search