Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
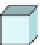
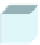
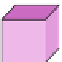
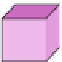
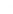
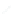
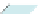
Fig. 6.
The three shapes S
3
, H
3
,andT
3
.
These two imaginary cubes have the same shape which we denote by S
n
(Fig.
6
).
Let
I
S
be the IFS that consists of 2
n−
1
homothetic transformations with the scale
1
/
2 that map
C
to the cubes in
S
n
, and let
S
n
∞
be the fractal induced by
I
S
.
S
n
is
∞
a fractal imaginary
n
-cube with the similarity dimension
n
−
1 by Proposition
11
.
We denote by S
n
∞
the shape of
S
n
∞
.TheshapeS
3
∞
is the Sierpinski tetrahedron.
Since all the components of
I
S
are homothetic transformations, the convex hull
of
S
n
∞
is equal to the convex hull of the centers of
I
S
,whichis
S
n
defined in
Sect.
3.3
.
It is immediate to show that
S
n
and
S
n
are the only two ways of selecting
2
n−
1
P
n
n
n
-cubes from
{
a
|
a
∈{
0
,
1
}
}
to form an imaginary cube. Therefore,
S
n
∞
is the only fractal imaginary cube shape obtained as the limit of an IFS that
is composed of 2
n−
1
homothetic transformations with the scale 1/2.
4.3 Fractal Imaginary Cubes
H
∞
and
T
∞
and Their
Higher-Dimensional Extensions
n
). We define
Q
n
We study the case
k
=3.Let
C
be the
n
-cube conv(
{−
1
,
1
}
a
ↂ
C
n
)as
3
(
C
+
(
a
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
{
2
a
}
). There are the following three ways of selecting
3
n−
1
n
-cubes from
Q
n
n
{
a
|
a
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
}
to form an imaginary cube of
C
.
H
n
=
Q
n
n
,
∪{
a
|
a
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
a
·
1
≡
0
(mod 3)
}
,
T
n
=
Q
n
n
,
∪{
a
|
a
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
a
·
1
≡−
1
(mod 3)
}
,
T
n
=
Q
n
n
,
∪{
a
|
a
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
a
·
1
≡
1
(mod 3)
}
.
T
n
and
T
n
have the same shape which we denote by
T
n
. We denote by
H
n
the
shape of
H
n
(Fig.
6
).
Let
I
H
(resp.
I
T
) be the IFS that consists of 3
n−
1
homothetic transformations
with the scale 1
/
3 that map
C
to the cubes in
H
n
(resp.
T
n
), and let
H
n
∞
(resp.
T
n
∞
) be the fractal induced by
I
H
(resp.
I
T
).
H
n
and
T
n
∞
are fractal imaginary
∞
1 by Proposition
11
. We write H
n
∞
n
-cubes with the similarity dimension
n
−
and T
n
∞
for their shapes.
The convex hull of
H
n
∞
is equal to the convex hull of the centers of the
components of
I
H
because they are homothetic transformations. It is the set
D
n
=
n
{
x
∈{−
1
,
0
,
1
}
|
x
·
1
≡
0
(mod 3)
}
.






























































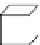
























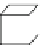







































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search