Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
3.4.2 Fractional transport rate of bed load
The pioneering research on the fractional transport rate of non-uniform sediment is
attributed to Einstein (1950). After that, Ashida and Michiue (1972), Parker
et al.
(1982), Misri
et al
. (1984), Samaga
et al
. (1986a), Bridge and Bennett (1992), Patel
and Ranga Raju (1996), and Wu
et al
. (2000b) proposed several methods to calculate
the fractional transport rate of non-uniform bed load. Hsu and Holly (1992) proposed
a method to compute the size composition of non-uniform bed load by considering the
probability and availability of moving sediment. Some of these methods are introduced
below.
Einstein formula
Einstein (1942, 1950) considered the probability of sediment transport due to the
fluctuation of turbulent flow and established sediment transport functions based on
fluid mechanics and probability theory. His bed-load function is graphically shown
in Fig. 3.14 and expressed as
(
1
/
7
)
∗
k
−
2
1
√
π
43.5
∗
k
e
−
t
2
dt
1
−
=
(3.71)
1
+
43.5
∗
k
−
(
1
/
7
)
∗
k
−
2
s
gd
k
]
2
x
where
, in which
q
b
∗
k
is the bed-load transport rate of size class
k
by weight per unit time and width,
∗
k
=
q
b
∗
k
/
[
p
bk
γ
(γ
/γ
−
1
)
, and
∗
k
=
ξ
b
Y
(β
/β
)
s
=
R
S
f
)
(γ
−
γ)
d
k
/(γ
,
ξ
b
and
Y
are the hiding and pressure correction factors for non-
s
.
R
is the hydraulic radius
due to grain roughness, determined using Einstein's movable bed roughness method.
uniform sediment,
β
=
log 10.6, and
β
=
log
(
10.6
X
/
)
x
s
s
is the apparent roughness of bed surface, and
=
k
s
/χ
s
, with
k
s
=
d
65
and
χ
s
s
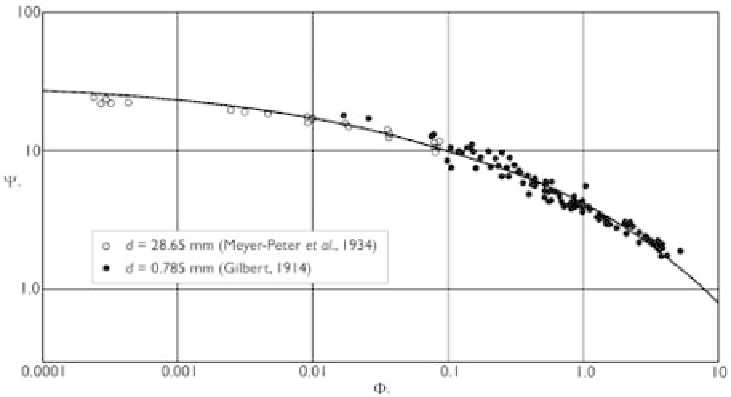
Figure 3.14
Einstein's (1950) bed-load function compared with uniform sediment data.