Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
where
c
is the critical shear stress for sediment incipient motion,
z
d
is the height at
which the bottom velocity acts on the particle,
k
s
is the bed roughness height, and
χ
s
is a correction factor related to the roughness Reynolds number
k
s
U
∗
/ν
τ
in general
situations and has a value of 1 for a hydraulic rough bed.
Because
C
D
,
C
L
, and
χ
s
are related to flow conditions, Eq. (3.31) can be rewritten as
τ
c
d
=
f
(
U
d
/ν)
(3.32)
∗
(γ
−
γ)
s
Eq. (3.32) was first proposed by Shields (1936). The dimensionless parameter
τ
/
[
(γ
−
γ)
d
]
, denoted as
c
, is often called the critical Shields number. Shields drew
c
s
a curve of
using his experimental data. However, the original
Shields curve did not have any measurement data in the range of small
R
e
∗
. Therefore,
many investigators, such as Yalin and Karahan (1979) and Chien and Wan (1983),
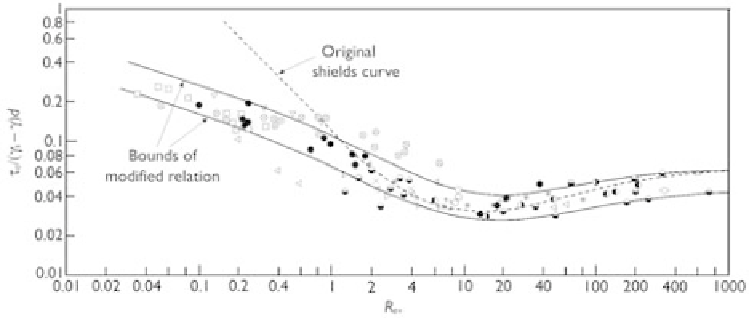
modified the original Shields curve using wider ranges of data. Fig. 3.7 shows the
Shields curve modified by Chien and Wan.
Because the relation between
c
and
R
e
∗
=
U
∗
d
/ν
c
and
R
e
∗
in Fig. 3.7 is not explicit, iteration is needed
to obtain the critical shear stress for a given sediment size. However, an explicit relation
between
2
1
/
3
can be
c
and the non-dimensional particle size
D
∗
=
d
[
(ρ
/ρ
−
1
)
g
/ν
]
s
obtained from Fig. 3.7. It is approximated by (Wu and Wang, 1999)
⎧
⎨
0.126
D
−
0.44
∗
,
D
∗
<
1.5
0.131
D
−
0.55
≤
D
∗
<
,
1.5
10
∗
0.0685
D
−
0.27
τ
c
,10
≤
D
∗
<
20
∗
d
=
(3.33)
0.0173
D
0.19
∗
(γ
−
γ)
⎩
, 0
≤
D
∗
<
40
s
0.0115
D
0.30
∗
, 0
≤
D
∗
<
150
0.052,
D
∗
≥
150
m
−
2
and m, respectively.
where
τ
c
and
d
are in N
·
Figure 3.7
Shields curve modified by Chien and Wan (1983).