Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
7.3.4 Examples
Case 1. Sediment transport in an 180
◦
channel bend
The flow, sediment transport, and bed change processes in an 180
◦
channel bend inves-
tigated experimentally by Odgaard and Bergs (1988) was simulated by Wu andWenka
(1998), Wu
et al
. (2000a), and Zeng
et al
. (2005) using 3-D models. The channel bend
was 80m long and 2.44m wide, connected with 20m long straight sections upstream
and downstream. The cross-section was trapezoidal with vertical sidewalls, and the
channel bed was filled with a 30 cm thick layer of sand with an initially flat surface.
The sand had a median diameter of 0.3mm and a geometric standard deviation of
1.45. The experiment was carried out at a discharge of 0.153m
3
s
−
1
with an aver-
age water depth of 0.15m and average velocity of 0.45m
s
−
1
. The sediment moved
·
cm
−
1
min
−
1
, as measured
through the channel mainly as bed load at a rate of 3.7 g
·
by a bed-load sampler.
Wu andWenka (1998) andWu
et al
. (2000a) used the 3-D flowmodel introduced in
Section 7.1.3.2 with the standard
k
-
ε
turbulence closure, whereas Zeng
et al
. (2005)
used a 3-D flow model with the
k
-
ω
turbulence closure. Wu
et al
. and Zeng
et al
.
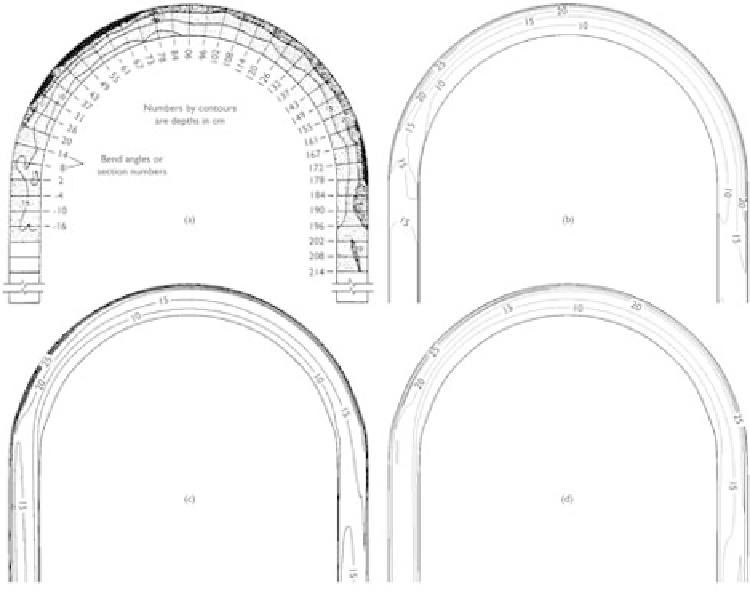
Figure 7.5
Flow depth contours in an 180
◦
bend: (a) measured by Odgaard and Bergs (1988),
(b) calculated by Zeng
et al
. (2005), (c) calculated by Wu and Wenka (1998), and
(d) calculated by Wu
et al
. (2000a).