Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
level set method can be found in Osher and Sethian (1988), while the MAC and VOF
methods are introduced below.
7.1.3.1 MAC and VOF methods
The general 2-D MAC method of Harlow and Welch (1965) introduced in
Section 4.4.1 can be easily extended to the 3-D case. The numerical discretization
and calculation procedure are not repeated here. The technique of handling the free
surface, which is not included in Section 4.4.1, is described below.
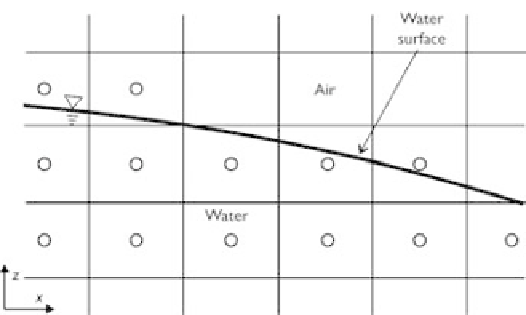
The MAC method adopts a fixed, Eulerian grid, which covers the fluid (water) area
and surrounding void (air) area. The location of fluid within the grid is determined
by a set of marker particles that move with the fluid, as shown in Fig. 7.1. Grid cells
containing markers are considered occupied by fluid, while those without markers are
void. A free surface is defined to exist in any grid cell that contains markers and has at
least one neighboring grid cell that is void. Evolution of the free surface is calculated
by moving the markers with locally interpolated flow velocities. At the free surface,
the air pressure is assigned to all surface cells, and velocity components are assigned
on or immediately outside the surface to satisfy the conditions of incompressibility
and zero shear stress.
Figure 7.1
Computational grid in MAC method.
The MAC method can successfully handle the breakup and coalescence of fluid
masses. The reason is that the markers track fluid volumes rather than surfaces directly.
Surfaces are simply the boundaries of the volumes so that surfaces may appear, merge,
or disappear as volumes break apart or coalesce. However, the MAC method has been
used primarily for 2-D models because it requires considerable memory and CPU time
to accommodate the necessary number of marker particles. Typically, an average of
16 markers in each grid cell is needed to insure an accurate tracking of surfaces under-
going large deformations. In addition, this method is inefficient in regions involving
converging and diverging flows with stagnation points.
To avoid the disadvantages of the MAC method, Hirt and Nichols (1981) proposed
the VOF method, which also employs volume tracking. The VOF method adopts the