Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
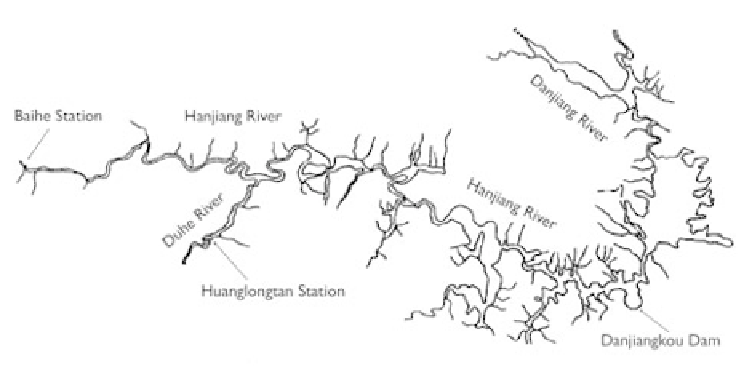
Figure 5.23
Sketch of Danjiangkou Reservoir.
study of the sedimentation process in the reservoir because the confluence is very close
to the dam.
The sedimentation process in the Hanjiang River branch was simulated. The com-
putational domain included a 188 km long reach in the main stream from the Baihe
Hydrology Station to the dam, and a 12 km long reach in the tributary Duhe River,
which joins the Hanjiang River 157 km upstream of the dam. Sixty-one cross-sections
were distributed along the main stream and four cross-sections in the tributary. The
simulation period encompassed 13 years, from 1968 to 1980. The Manning roughness
coefficient and bed-material porosity were estimated using measurement data. The
sediment transport capacity was determined using the Wu
et al
. (2000b) formula. The
flocculation of fine sediments (
d
0.01 mm) was considered using the Migniot (1968)
relation, which is described in Section 11.1.2.
Fig. 5.24 shows the calculated and measured annual sediment depositions in differ-
ent years, while Fig. 5.25 shows the calculated and measured longitudinal distributions
of sediment deposition accumulated from 1968 to 1979. In order for the influence of
the adaptation coefficient
<
α
on the amounts of deposition to be investigated, it was
given four constant values: 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.5, and calculated using the Armanini-
di Silvio (1988) method. The values 0.5 and 1.0 and the Armanini-di Silvio method
provide good predictions. In particular, the results obtained using the Armanini-di
Silvio method and the constant value of 1.0 for
are very close.
The effect of the mixing layer thickness was also verified by specifying it as half the
dune height and two constant values of 0.05 and 0.25 m. The calculated deposition
amounts and longitudinal distributions are not sensitive to the mixing layer thickness,
as found in Case 2. The simulation results are not shown here.
In summary, in the case of channel degradation, the computed equilibrium scour
depth and bed-armoring process are not particularly sensitive to the adaptation length
(coefficient), but are affected by the mixing layer thickness. In the case of channel
α