Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
for a complexmodel system, because the governing equations and boundary conditions
may be discretized using numerical schemes with different accuracies. An alternative
method to analyze the accuracy is through the computation of solution errors on a
series of meshes with grid spacings of
x
,2
x
,3
x
, etc. The root-mean-square error
for the solution on each grid is defined as
N
2
N
1
/
2
f
i
−
f
i
)
R
f
=
1
(
(4.6)
i
=
The error
R
f
is related to the grid spacing
x
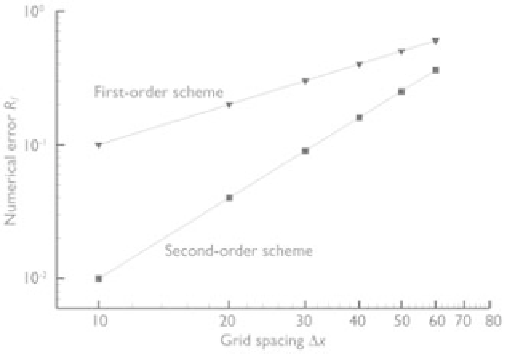
, as shown in Fig. 4.2. This relationship
can be represented by
x
m
R
f
=
a
(4.7)
where
a
is a nearly constant coefficient. The value of
m
can be determined from the
series of
R
f
and
x
pair values using a regression method.
Figure 4.2
Relation between
R
f
and
x
.
Performing the above numerical accuracy analysis requires that the exact solution
be known in advance. This is not feasible for most problems in river engineering.
However, the prescribed solution forcing (PSF) method (Dee
et al
., 1992) can be used
instead. The PSF method substitutes the unknown function
f
in Eq. (4.1) by a known
function
p
. The new equation for
p
has the form:
S
∗
L
(
p
;
x
)
=
(4.8)
where
S
∗
is the new source term, which might be different from
S
because
p
may not
be the exact solution of Eq. (4.1). Note that it is preferable that the function
p
satisfies