Database Reference
In-Depth Information
What is Oracle Instance Memory Architecture?
By saying, memory architecture of Oracle Instance we mean
how RAM is utilized by Oracle Instance or more precisely part
of RAM is dedicated for Oracle purpose, since its not only
Oracle that is utilizing the RAM in your computer. Every
program that you run under any OS (Windows, Linux etc.)
occupies certain amount of RAM. For example, if your computer
has 256MB of RAM and let's suppose MS Word occupies 50
MB. If you keep on opening MS Word instances your system
will turn slower and slower and eventually will halt. Every
software that you run, utilizes RAM for speedy processing and
when it comes to making changes permanent (when you press
the save button etc.) that software writes the stuff in the hard
disk.
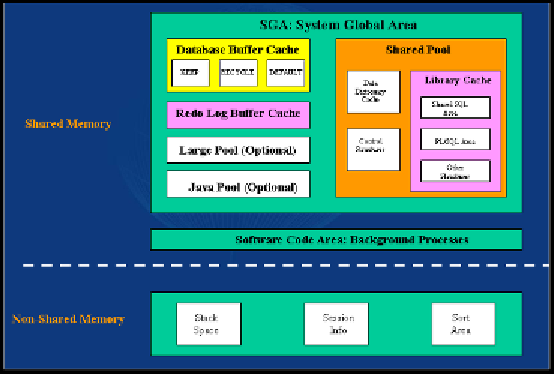
Figure 4-6: Memory architecture of Oracle Instance. It's the area of the
computer memory (RAM) occupied by Oracle Instance for requests
processing. Every software that you run under any OS occupies RAM
(or Memory), so does Oracle. SGA is the most important piece and it
stands for System Global Area. Non-shared memory is not shared
among all the users whereas shared is shared among all. Database
Buffer Cache has three sub-caches: KEEP, RECYCLE, DEFAULT.
Three different states of buffers within Database Buffer Cache: Dirty
Buffers, Free Buffers, Pinned Buffers. Non-Shared part of Oracle
Search WWH ::

Custom Search