Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
100+
90-94
80-84
70-74
60-64
50-54
40-44
30-34
20-24
10-14
00-04
15,000
10,000
5,000
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
Pop. (thousands)
Men
Women
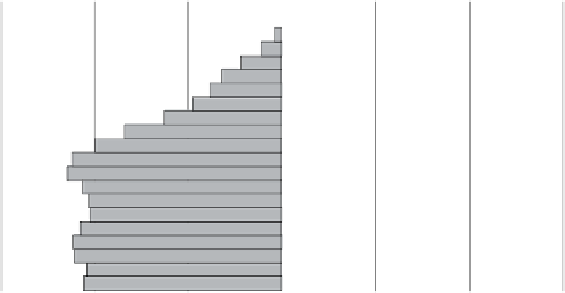
Figure 3.4.
US population pyramid 2005
(Source : UN, Population Division)
The number of seniors (65+) increased from 9.8% to 12.3% of the total
population between 1970 and 2005. Since then, however, the population of working
age people (aged 15 to 64) also greatly increased, going from under 130 million to
over 200 million people, and the number of children (under 15) dropped from 28.3%
to 20.8% of the population. This made the dependency ratio
1
registered by the
United Nations decline from 62% in 1970, to 49% in 2005.
This demographic dividend is an important factor of economic growth since
rapid job creation maintains unemployment rates at a low level (4.5%). The
immigration of young adults significantly strengthens the available workforce in the
United States. As they apprehend poor job market prospects for the year 2030
because of the large share of postwar baby boomers in the US manpower, authorities
seem, therefore, reluctant to enforce laws against businesses that hire illegal
immigrants.
1
. The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of people under the age of 15 years, or over
the age of 64, and people between the ages of 15 and 64. In developing countries, the
dependency rate is high because of the large number of children (young-age dependency). In
older countries like Japan or Italy, this ratio increases due to the increase in the proportion of
elders in the total population (old-age dependency). For economists, countries having the
highest proportion of working age population benefit from a “demographic dividend” (15 to
64 years as the standard reference). This is the case in China today, as well as in the United
States.