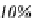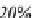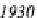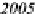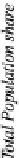Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
From the Atlantic to the Pacific, the country has very simple, yet strikingly vast,
structural areas. The territory forms a rectangular block of 7.7 million km² which
lies between 67°W and 125°W longitude and spans 4 time zones. New York is
barely closer to San Francisco than it is to Ireland. From east to west, the 45th
parallel crosses the country over nearly 4,500 km. In latitude, the country stretches
from the 24th parallel North at the tip of Florida, to just a stone's throw from the
49th parallel North, which was adopted under a treaty with England in 1846 as the
official border between the United States and Canada, west of the Mississippi all the
way to the Pacific coast. From north to south the 100th meridian crosses the country
for more than 2,500 km between Mexico and Canada. With its continental mass and
its position in latitude, the United States territory is quite similar to the territory of
China, with one major difference: it shares borders with the ocean on three sides
along nearly 40,000 km of its coastline. This long coastal played a considerable role
in the settlement of the United States.
Figure 1.2.
Population share living within 100 km of an ocean or the Great Lakes
The Atlantic Ocean coast is the longest, with nearly 23,500 km, and follows a
very jagged coastline from the tip of Florida to Maine, and 2,600 km in a straight
line from Key West to the Canadian border. The Atlantic Ocean extends south and
merges with the vast Gulf of Mexico. Less uneven than the Atlantic coast, the Gulf
Coast is more than 8,300 km in length. Over 18,100 km long, the Pacific coastline
stretches over 1,900 km in a straight line between San Diego and Vancouver. In
addition to these three ocean fronts, the five freshwater Great Lakes at the Canadian
border form a veritable inland sea stretching over nearly 250,000 km², and greatly
influencing the climate of the Northeast. The majority of the US population now
resides in a “coastal region”, defined by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration (NOAA) as a place usually located within 100 km of one of the three
ocean fronts or the Great Lakes (see Figure 1.2). In 2005, the average population
density of these coastal regions reached 118 inhabitants/km², compared to only
22 inhabitants/km² for the “inland” regions in the conterminous 48 states. Although