Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Performance of Branch Schemes
What is the effective performance of each of these schemes? The effective pipeline speedup
with branch penalties, assuming an ideal CPI of 1, is
Because of the following:
we obtain:
The branch frequency and branch penalty can have a component from both unconditional
and conditional branches. However, the later dominate since they are more frequent.
Example
For a deeper pipeline, such as that in a MIPS R4000, it takes at least three
pipeline stages before the branch-target address is known and an additional
cycle before the branch condition is evaluated, assuming no stalls on the re-
gisters in the conditional comparison. A three-stage delay leads to the branch
penalties for the three simplest prediction schemes listed in
Figure C.15
.
FIGURE C.15
Branch penalties for the three simplest prediction schemes
for a deeper pipeline
.
Find the effective addition to the CPI arising from branches for this pipeline,
assuming the following frequencies:


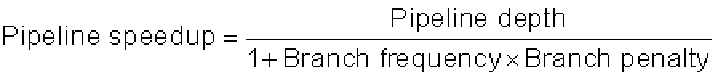

Search WWH ::

Custom Search