Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
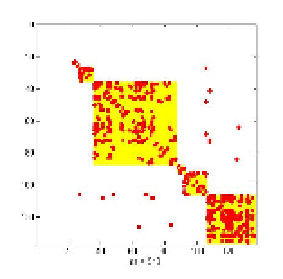
Fig. 18. Phone-call network: (a) adjacency matrix is marked by red dots, all possible
intra-communities links are shown by yellow squares. Links predicted by dynamics (blue
dots) tend to concentrate within communities: (b)
t
=
=
10;
(c)
t
15.
has the lower computational complexity than
S
(
i
,
i
)
,itmakes
S
(
i
,
i
)
DC
(
k
,
n
)
CC
(
k
,
n
)
more suitable for
CC
(
)
KC
(
)
large networks.
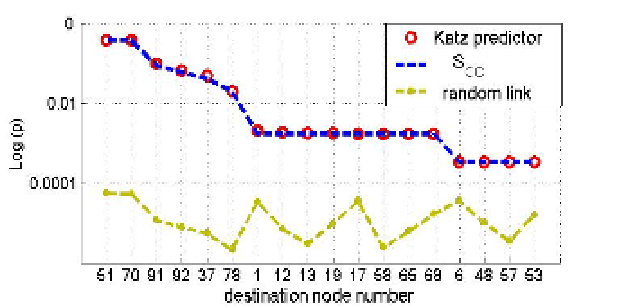
calculated according to (32)
for cases with intra- and inter-communities links in the phone-call network are depicted at
Fig.19. Here the scores are normalized as probabilities and sorted according to its priority;
destination nodes
n
are listed along the
x
-axis; corresponding random-link probabilities,
p
kn
=(
Prediction scores
S
129,
n
and
S
129,
n
)
/2
m
, are shown as the reference. Note that the link with the highest priority,
{129,51} for
S
(
i
,
i
)
d
k
d
n
CC
(
)
, is the same as in the intra-community recommendation (cf. Table 2).
However, the presence of inter-community links modifies priorities of other recommendations
according to (30). To make verification we compare the predicted links at the phone-call
network with links observed for the user "129" at the BT proximity layer. This comparison
shows a good fit: 16 out of 18 predicted links are found at the BT proximity layer.
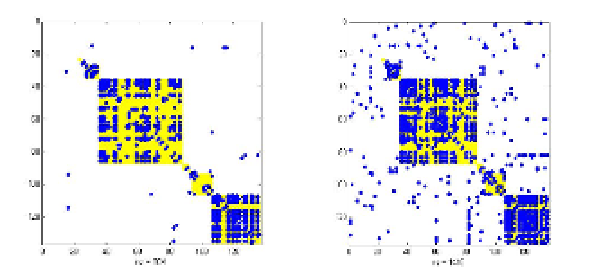
Results for the combined BT and phone-calls networks are presented at Fig.20. Pair-wise
correlations between nodes obtained by dynamical systems approach are shown at Fig.20 (a).
These correlations may be interpreted as probabilities for new links recommendations. Fig.20
(b) depicts recommended links based on the modified Katz predictor (blue circles) beyond the
k
,
n
Fig. 19. Priorities of the FoF recommendations for the user 129 at Fig.12 to be connected to
destination nodes shown along
x
-axis over all relevant communities.