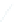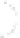Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
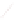
In the frequency domain the analytic complex signal, its complex conjugate signal, real and
imaginary components are related as follows:
1
2
1
2
jn
jn
jn
Xe
Xe
Xe
R
jn
jn
jn
jX
e
X e
X
e
(8)
I
jn
jn
2
Xe
2
jXe
,
0
2
R
I
S
jn
Xe
0,
2
0
S
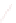
Discrete-time complex signals are easily processed by digital complex circuits, whose
transfer functions contain complex coefficients (Márquez, 2011).
An output complex signal
Y
C
(
z
) is the response of a complex system with transfer function
H
C
(
z
), when complex signal
X
C
(
z
) is applied as an input. Being complex functions,
X
C
(
z
),
Y
C
(
z
) and
H
C
(
z
), can be represented by their real and imaginary parts:
Yz
H z
X z
C
C
C
(9)
Y
z
jY
z
H
z
jH
z
X
z
jX
z
R
I
R
I
R
I
After mathematical operations are applied, the complex output signal and its real and
imaginary parts become:
Yz
H z jHz X z jXz
H
C
R
I
R
I
zX
z
H zX z
j H zX
z
H
zX z
(10)
R
R
I
I
I
R
R
I
Yz
Yz
R
I
According to equation (10), the block-diagram of a complex system will be as shown in
Fig. 4.
X
R
(
z
)
+
Y
R
(
z
)
H
R
(
z
)
H
I
(
z
)
H
I
(
z
)
X
I
(
z
)
Y
I
(
z
)
+
H
R
(
z
)
Fig. 4. Block-diagram of a complex system