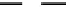Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Bit-L
evel F
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
u
m 1
0
u
m 1
1
D
Q
D
Q
C
i
C
o
C
i
C
o
A
A
∑
∑
B
DQ
B
DQ
'0'
'0'
c
i
a
b
b
a
b
c
i
b
c
o
c
i
a
a
s
o
a
a
c
i
b
a
b
b
a
b
c
i
c
i
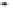
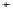
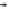
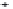
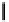
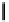
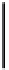
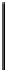
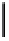
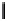
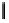
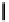
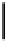
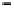
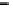
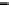
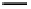
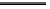
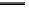
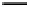
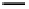
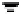
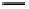
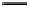
Fig. 3. Transistor-level implementation of the Full Adder Cell.
is factored along two axes in the image plane: the azimuth or cross-range coordinate
(horizontal axis,
x
) and the slant range (vertical axis,
y
), respectively. The conventional
triangular,
r
(
y
), and Gaussian approximation,
a
(
x
)=exp(-(
x
)
2
/
a
2
) with the adjustable
fractional parameter
a
, are considered for the SAR range and azimuth ambiguity function
(AF), (Wehner, 1994). In analogy to the image reconstruction, we employed the quality
metric defined as an improvement in the output signal-to-noise ratio (IOSNR)
2
K
ˆ
(
MSF
)
b
b
k
k
k
1
IOSNR = 10
log
10
;
p
= 1, 2
(26)
2
K
ˆ
()
p
b
b
k
k
k
1
ˆ
MSF
k
(
)
where
b
represents the value of the k
th
element (pixel) of the original image
B
,
b
represents the value of the k
th
element (pixel) of the degraded image formed applying the
MSF technique (19), and
ˆ
p
()
k
b
represents a value of the k
th
pixel of the image reconstructed
with two developed methods,
p
= 1, 2, where
p
= 1 corresponds to the RSF algorithm and
p
=
2 corresponds to the RASF algorithm, respectively.
The quality metrics defined by (26) allows to quantify the performance of different image
enhancement/reconstruction algorithms in a variety of aspects. According to these quality
metrics, the higher is the
IOSNR
, the better is the improvement of the image
enhancement/reconstruction with the particular employed algorithm.
4.2 RS implementation results
The reported RS implementation results are achieved with the VLSI-FPGA architecture
based on MPPAs, for the enhancement/reconstruction of RS images acquired with different