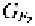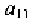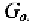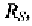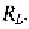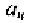Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.3 THE ROSENSTARK METHOD
Now we will try to express the transfer function obtained by
considering the signal flow analysis, in a form which is more similar to the
result given in (3.1b). Indeed, (3.5) can be rewritten as
This form is exactly that found by Rosenstark and allows us to elaborate its
procedure. Except for term
in the numerator, it is similar to relationship
(3.1b).
The Rosenstark method is based on the calculation of the
return ratio, T,
the
asymptotic term,
and the
direct transmission term,
All these
quantities, must be calculated with respect to one and only one controlled
source within the feedback amplifier. Moreover, they are a function of the
specific input and output conditions, which means they depend on the input
source resistance, and output load resistance, The exact input-output
transfer function of the feedback amplifier is thus given by [R74]
The three quantities in (3.7) are directly related to the weights and
parameter
P
of the flow graph through the following relationships obtained
by comparing (3.6) and (3.7)
Hence, to evaluate the three terms, we have to refer a controlled source
quantity,
to a controlling quantity,
by a parameter
P
and follow the
steps given below: