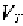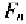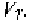Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
In this case, after applying a voltage to the gate, border effects deplete a
wider region thus increasing the threshold voltage. This effect is modeled by
adding the term
to theoriginal
in(1.35).
is a corrective
factor that approaches zero in the case of wide channels.
Taking into account (1.72) and (1.73) the final form for the threshold
voltage becomes
1.3.9.7
Hot carrier effects
High lateral electric fields can generate high velocity carriers also called
hot carriers. In short-channel devices, due to their high velocity, electron-
hole pairs can be generated in the channel by impact ionization and
avalanching. As a consequence, in n-MOS, a current of holes can flow from
the drain to the substrate. This effect can be viewed as a finite resistance that
connects the drain to the substrate and can result in a major limitation when
realizing high impedance cascode structures.
Moreover, some hot carriers with enough energy can tunnel the gate
oxide thus causing either a dc gate current or, if trapped in the oxide, a
threshold voltage alteration. This latter phenomenon can drastically limit the
long-term reliability of MOS transistors.
A further hot carrier effect is the so-called punch-through. It happens
when the depletion regions of source and drain are so close each other that
hot carriers with enough energy can overcome the short-channel region thus
causing a current that is no longer limited by the drift equations. It is as if the
channel were no longer present in the device and both source and drain areas
were connected together. This phenomenon is limited by increasing the
substrate doping which consequently limits the depletion region extensions.
This effect not only lowers drain impedance but can also cause transistor
breakdown.
1.3.10
Sub-threshold Region
In our previous modeling we assumed that no conduction could exist if
the gate voltage is below the threshold. Actually, when the gate voltage is
increased over the threshold, there is not an abrupt transition from the cut-off
region to any of the conducting region. Specifically, a small drain current
can flow at gate voltages a few millivolts below In this condition, the
device is said to operate in sub-threshold or in weak inversion region and the
current has an exponential relationship with the voltage applied.
Assuming long channel devices, the drain current is well expressed by [9]