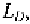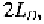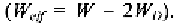Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The resulting small signal model is shown in Fig. 13.
1.3.9
Second Order Effects in MOSFET Modeling
The main second order effects that should be taken into account when
determining a MOS large signal model are reported in this section. Their
effects are always present but are especially prominent in short-channel
devices and, often, cannot be ignored.
In the following we shall neglect the subscript
n,
which referred to n-
MOS transistors.
1.3.9.1
Channel length reduction due to overlap
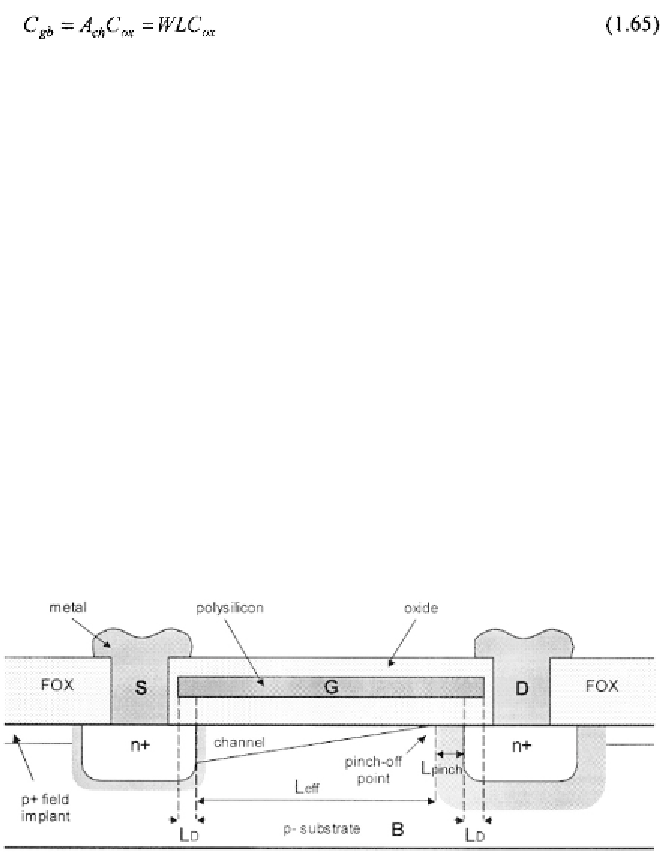
Referring to Fig. 1.11, we see that designed channel,
L,
is reduced due to
the overlap. Assuming a symmetric device with equal overlap,
at both
the source and the drain, the amount of reduction is equal to
that is, the
effective channel length,
is equal to
Obviously, the influence of the overlap is greater in short channel devices
as it strongly affects the real channel. As a consequence, in all the previous
equations, (1.66) should be used for the channel length.
A similar equation holds for the width,
W,
as well
However, this effect is less frequent since minimum MOS widths are hardly
chosen especially in analog designs. Thus we can assume