Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
and
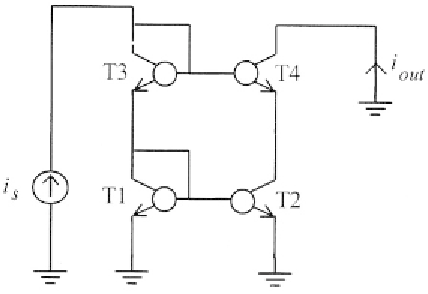
9.3 THE CASCODE CURRENT MIRROR
The cascode current mirror avoids the drawbacks of the Wilson mirror by
realising a symmetrical topology which sets the Z-to-X voltages of
transistors T1 and T2 almost equal, thereby minimising errors due to the
finite transistor output resistance [AH87], [GT86]. The AC schematic of the
cascode current mirror is shown in Fig. 9.8. Note that in this case, the circuit
behaviour is not based on feedback. Rather, its improved performance is
achieved thanks to the current-buffering action of the cascode transistor T4.
In this manner, the accuracy of the current gain and the output resistance are
increased. In the following we will not analyse these characteristics, as they
seem self-evident. Instead, we will concentrate our attention on a special
effect due to a local feedback that arises only in a bipolar implementation.
As we will see, this effect slightly reduces the achievable output resistance.