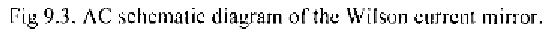Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Finally, we find the well-known result for the output resistance of a
differential stage [GM93], [LS94], [JM97]
9.2 THE WILSON CURRENT MIRROR
Among the several current mirror topologies, the Wilson current mirror is
a high-performance solution which is heavily based on a negative-feedback
configuration, [W90], [W901]. The AC schematic diagram of the Wilson
current mirror is depicted in Fig. 9.3 (again, bulk connections are omitted for
simplicity). Note that although the circuit is described using the generic
transistor, in common practice it is more frequently encountered in its
bipolar implementation. In fact, as transistors T1 and T2 work with
substantially different Z-to-X voltages, this can cause offset and gain error
especially with MOS processes in which the channel length modulation is
more significant than the corresponding Early effect of bipolar transistors.
The feedback mechanism can simply be explained as follows: the output
current, is collected into the input of current mirror T2-T1, and is then
fed back to the mirror input so it can be subtracted from the input signal,
(negative shunt-series feedback)
To simplify the analysis, consider the mixed model of the circuit under
consideration shown in Fig. 9.4, where small-signal models of transistors T1
and T2 are drawn. Note also that the diode-connected transistor T2 is