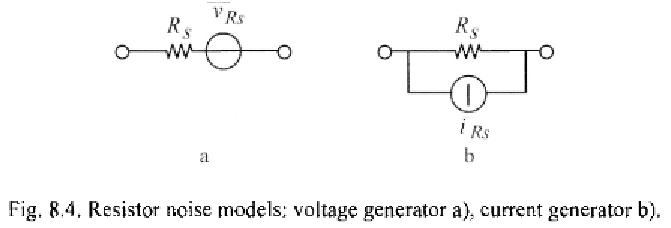
Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Transistor
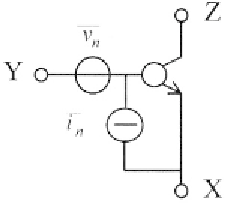
Transistors contain several independent sources of noise. These sources
can be referred to the input port (terminals Y-X of the generalised transistor)
in order to be modeled by two noise generators according to the procedures
described in the previous paragraph. Thus, the generalised transistor model
introduced in Chapter 2 is now modified to include the equivalent input
noise generators,
and
as depicted in Fig. 8.5
It can be shown that noise magnitude depends on the transistor operating
point, and that both the noise sources are important for BJTs, while the
voltage source is dominant in FETs at low frequencies. However, the FET
noise voltage is higher than that of the BJTs.
Operational Amplifier
Operational amplifiers can be arranged in inverting, noninverting, and
differential closed-loop configurations. Thus all of these configurations must
be adequately represented by an opamp noise model. Opamps exhibit two
input ports and consequently they must be modeled by four noise generators,
as illustrated in Fig. 8.6. Since virtually any opamp input
stage is implemented by a differential amplifier which is characterised by a